Sparse linear modeling of next-generation mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) data for isoform discovery and abundance estimation
- PMID: 22135461
- PMCID: PMC3250192
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1113972108
Sparse linear modeling of next-generation mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) data for isoform discovery and abundance estimation
Abstract
Since the inception of next-generation mRNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) technology, various attempts have been made to utilize RNA-Seq data in assembling full-length mRNA isoforms de novo and estimating abundance of isoforms. However, for genes with more than a few exons, the problem tends to be challenging and often involves identifiability issues in statistical modeling. We have developed a statistical method called "sparse linear modeling of RNA-Seq data for isoform discovery and abundance estimation" (SLIDE) that takes exon boundaries and RNA-Seq data as input to discern the set of mRNA isoforms that are most likely to present in an RNA-Seq sample. SLIDE is based on a linear model with a design matrix that models the sampling probability of RNA-Seq reads from different mRNA isoforms. To tackle the model unidentifiability issue, SLIDE uses a modified Lasso procedure for parameter estimation. Compared with deterministic isoform assembly algorithms (e.g., Cufflinks), SLIDE considers the stochastic aspects of RNA-Seq reads in exons from different isoforms and thus has increased power in detecting more novel isoforms. Another advantage of SLIDE is its flexibility of incorporating other transcriptomic data such as RACE, CAGE, and EST into its model to further increase isoform discovery accuracy. SLIDE can also work downstream of other RNA-Seq assembly algorithms to integrate newly discovered genes and exons. Besides isoform discovery, SLIDE sequentially uses the same linear model to estimate the abundance of discovered isoforms. Simulation and real data studies show that SLIDE performs as well as or better than major competitors in both isoform discovery and abundance estimation. The SLIDE software package is available at https://sites.google.com/site/jingyijli/SLIDE.zip.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
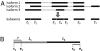


 of 798 isoforms on 50 simulated datasets. p, true isoform proportion; median
of 798 isoforms on 50 simulated datasets. p, true isoform proportion; median  , median of the 50 estimated isoform proportions. (B) SLIDE vs. SIIER estimates of the 798 isoforms on dataset 1. (C) SLIDE vs. Cufflinks estimates of the 798 isoforms on dataset 1.
, median of the 50 estimated isoform proportions. (B) SLIDE vs. SIIER estimates of the 798 isoforms on dataset 1. (C) SLIDE vs. Cufflinks estimates of the 798 isoforms on dataset 1.
Similar articles
-
NMFP: a non-negative matrix factorization based preselection method to increase accuracy of identifying mRNA isoforms from RNA-seq data.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jan 11;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2304-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26818007 Free PMC article.
-
Freddie: annotation-independent detection and discovery of transcriptomic alternative splicing isoforms using long-read sequencing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 25;51(2):e11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1112. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36478271 Free PMC article.
-
Improving RNA-Seq expression estimation by modeling isoform- and exon-specific read sequencing rate.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Oct 16;16:332. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0750-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26475308 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell RNAseq for the study of isoforms-how is that possible?Genome Biol. 2018 Aug 10;19(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1496-z. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30097058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergism of proteomics and mRNA sequencing for enzyme discovery.J Biotechnol. 2016 Oct 10;235:132-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.12.015. Epub 2015 Dec 18. J Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26707808 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic data reveal the flavonoid biosynthesis metabolic pathway in Perilla frutescens (L.) leaves.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 1;10(1):16207. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73274-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33004940 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Sequencing and Analysis.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015 Apr 13;2015(11):951-69. doi: 10.1101/pdb.top084970. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015. PMID: 25870306 Free PMC article.
-
Improving PacBio long read accuracy by short read alignment.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046679. Epub 2012 Oct 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056399 Free PMC article.
-
Information transduction capacity reduces the uncertainties in annotation-free isoform discovery and quantification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 6;45(15):e143. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx585. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28911101 Free PMC article.
-
Inference of alternative splicing from RNA-Seq data with probabilistic splice graphs.Bioinformatics. 2013 Sep 15;29(18):2300-10. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt396. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23846746 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

