Regulation of immune responses by mTOR
- PMID: 22136167
- PMCID: PMC3616892
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075024
Regulation of immune responses by mTOR
Abstract
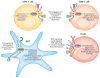
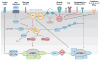
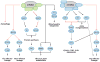
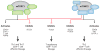
mTOR is an evolutionarily conserved serine/threonine kinase that plays a central role in integrating environmental cues in the form of growth factors, amino acids, and energy. In the study of the immune system, mTOR is emerging as a critical regulator of immune function because of its role in sensing and integrating cues from the immune microenvironment. With the greater appreciation of cellular metabolism as an important regulator of immune cell function, mTOR is proving to be a vital link between immune function and metabolism. In this review, we discuss the ability of mTOR to direct the adaptive immune response. Specifically, we focus on the role of mTOR in promoting differentiation, activation, and function in T cells, B cells, and antigen-presenting cells.
Figures



References
-
- Mills RE, Jameson JM. T cell dependence on mTOR signaling. Cell Cycle. 2009;8:545–48. - PubMed
-
- Weichhart T, Saemann MD. The multiple facets of mTOR in immunity. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:218–26. - PubMed
-
- Vezina C, Kudelski A, Sehgal SN. Rapamycin (AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. I Taxonomy of the producing streptomycete and isolation of the active principle. J Antibiot. 1975;28:721–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

