Structural and physical properties of antibacterial Ag-doped nano-hydroxyapatite synthesized at 100°C
- PMID: 22136671
- PMCID: PMC3240665
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-6-613
Structural and physical properties of antibacterial Ag-doped nano-hydroxyapatite synthesized at 100°C
Abstract
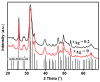
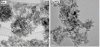
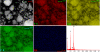
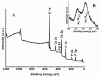
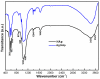
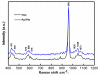
Synthesis of nanosized particle of Ag-doped hydroxyapatite with antibacterial properties is in the great interest in the development of new biomedical applications. In this article, we propose a method for synthesized the Ag-doped nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite. A silver-doped nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite was synthesized at 100°C in deionized water. Other phase or impurities were not observed. Silver-doped hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (Ag:HAp) were performed by setting the atomic ratio of Ag/[Ag + Ca] at 20% and [Ca + Ag]/P as 1.67. The X-ray diffraction studies demonstrate that powders made by co-precipitation at 100°C exhibit the apatite characteristics with good crystal structure and no new phase or impurity is found. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations suggest that these materials present a little different morphology, which reveals a homogeneous aspect of the synthesized particles for all samples. The presence of calcium (Ca), phosphor (P), oxygen (O), and silver (Ag) in the Ag:HAp is confirmed by energy dispersive X-ray (EDAX) analysis. FT-IR and FT-Raman spectroscopies revealed that the presence of the various vibrational modes corresponds to phosphates and hydroxyl groups. The strain of Staphylococcus aureus was used to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the Ca10-xAgx(PO4)6(OH)2 (x = 0 and 0.2). In vitro bacterial adhesion study indicated a significant difference between HAp (x = 0) and Ag:HAp (x = 0.2). The Ag:Hap nanopowder showed higher inhibition.
Figures

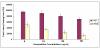
Similar articles
-
Effect of silver ion and silicate group on the antibacterial and antifungal properties of nanosized hydroxyapatite.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 26;14(1):29339. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80303-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39592678 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of silver doped hydroxyapatite nanocomposite coatings and evaluation of their antibacterial and corrosion resistance properties in simulated body fluid.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016 Dec 1;69:675-84. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2016.07.057. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016. PMID: 27612761
-
Structural properties of silver doped hydroxyapatite and their biocompatibility.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013 Apr 1;33(3):1395-402. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.042. Epub 2012 Dec 16. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013. PMID: 23827587
-
Simulation and Computer Study of Structures and Physical Properties of Hydroxyapatite with Various Defects.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Oct 17;11(10):2752. doi: 10.3390/nano11102752. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal Ion-Doped Hydroxyapatite-Based Materials for Bone Defect Restoration.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;10(12):1367. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10121367. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38135958 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Facile Preparative Access to Bioactive Silicon Oxycarbides with Tunable Porosity.Materials (Basel). 2019 Nov 22;12(23):3862. doi: 10.3390/ma12233862. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31766736 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Different Antibiotics Enhanced with Silver-Doped Hydroxyapatite Thin Films.Materials (Basel). 2016 Sep 16;9(9):778. doi: 10.3390/ma9090778. Materials (Basel). 2016. PMID: 28773899 Free PMC article.
-
A solid-state NMR study of selenium substitution into nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 19;16(5):11452-64. doi: 10.3390/ijms160511452. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25997001 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of Zinc Ions Using Hydroxyapatite and Study of Ultrasound Behavior of Aqueous Media.Materials (Basel). 2018 Aug 3;11(8):1350. doi: 10.3390/ma11081350. Materials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30081467 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Evaluation of Silver Concentrations in Hydroxyapatite Powders.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Sep 11;14(9):467. doi: 10.3390/jfb14090467. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37754881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dorozhkin SV. Calcium orthophosphates in nature, biology and medicine. Materials. 2009;2:399–498. doi: 10.3390/ma2020399. - DOI
-
- Vallet-Regí M, González-Calbet JM. Calcium phosphates as substitution of bone tissues. Progress Solid State Chem. 2004;32:1–31. doi: 10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2004.07.001. - DOI
-
- Hench LL. Bioceramics. J Am Ceram Soc. 1998;81:1705–1728.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

