Erythroid/myeloid progenitors and hematopoietic stem cells originate from distinct populations of endothelial cells
- PMID: 22136929
- PMCID: PMC3576591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.10.003
Erythroid/myeloid progenitors and hematopoietic stem cells originate from distinct populations of endothelial cells
Erratum in
- Cell Stem Cell. 2012 Mar 2;10(3):345-6
Abstract
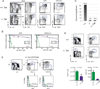
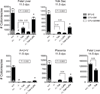
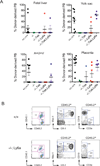
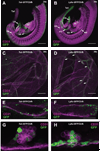
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and an earlier wave of definitive erythroid/myeloid progenitors (EMPs) differentiate from hemogenic endothelial cells in the conceptus. EMPs can be generated in vitro from embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cells, but efforts to produce HSCs have largely failed. The formation of both EMPs and HSCs requires the transcription factor Runx1 and its non-DNA binding partner core binding factor β (CBFβ). Here we show that the requirements for CBFβ in EMP and HSC formation in the conceptus are temporally and spatially distinct. Panendothelial expression of CBFβ in Tek-expressing cells was sufficient for EMP formation, but was not adequate for HSC formation. Expression of CBFβ in Ly6a-expressing cells, on the other hand, was sufficient for HSC, but not EMP, formation. The data indicate that EMPs and HSCs differentiate from distinct populations of hemogenic endothelial cells, with Ly6a expression specifically marking the HSC-generating hemogenic endothelium.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Boisset JC, van Cappellen W, Andrieu-Soler C, Galjart N, Dzierzak E, Robin C. In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium. Nature. 2010;464:116–120. - PubMed
-
- Bollerot K, Romero S, Dunon D, Jaffredo T. Core binding factor in the early avian embryo: cloning of Cbfbeta and combinatorial expression patterns with Runx1. Gene Expr Patterns. 2005;6:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Cai Z, de Bruijn MFTR, Ma X, Dortland B, Luteijn T, Downing JR, Dzierzak E. Haploinsufficiency of AML1/CBFA2 affects the embryonic generation of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Immunity. 2000;13:423–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

