Chemical genetic screen for AMPKα2 substrates uncovers a network of proteins involved in mitosis
- PMID: 22137581
- PMCID: PMC3246132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.005
Chemical genetic screen for AMPKα2 substrates uncovers a network of proteins involved in mitosis
Abstract
The energy-sensing AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is activated by low nutrient levels. Functions of AMPK, other than its role in cellular metabolism, are just beginning to emerge. Here we use a chemical genetics screen to identify direct substrates of AMPK in human cells. We find that AMPK phosphorylates 28 previously unidentified substrates, several of which are involved in mitosis and cytokinesis. We identify the residues phosphorylated by AMPK in vivo in several substrates, including protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12C (PPP1R12C) and p21-activated protein kinase (PAK2). AMPK-induced phosphorylation is necessary for PPP1R12C interaction with 14-3-3 and phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain. Both AMPK activity and PPP1R12C phosphorylation are increased in mitotic cells and are important for mitosis completion. These findings suggest that AMPK coordinates nutrient status with mitosis completion, which may be critical for the organism's response to low nutrients during development, or in adult stem and cancer cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
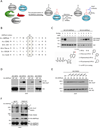

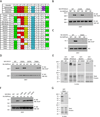
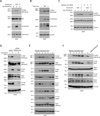
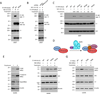

Comment in
-
Ramping up mitosis: an AMPKα2-regulated signaling network promotes mitotic progression.Mol Cell. 2012 Jan 13;45(1):8-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.12.018. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22244327
-
AMPK moonlights in mitosis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan 18;13(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrm3275. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22251904 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alaimo PJ, Shogren-Knaak MA, Shokat KM. Chemical genetic approaches for the elucidation of signaling pathways. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2001;5:360–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG026648/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EB001987/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- AG032837/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG31198/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG026648/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RR01614/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HG3456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AG032837/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG031198/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB001987/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031198/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ES153393/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM068762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM068762/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003456/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001614/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127088492/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 GM056203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

