Genetic background effects on age-related hearing loss associated with Cdh23 variants in mice
- PMID: 22138310
- PMCID: PMC3277672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2011.11.007
Genetic background effects on age-related hearing loss associated with Cdh23 variants in mice
Abstract
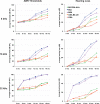
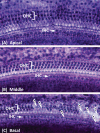
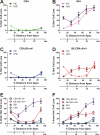
Inbred strain variants of the Cdh23 gene have been shown to influence the onset and progression of age-related hearing loss (AHL) in mice. In linkage backcrosses, the recessive Cdh23 allele (ahl) of the C57BL/6J strain, when homozygous, confers increased susceptibility to AHL, while the dominant allele (Ahl+) of the CBA/CaJ strain confers resistance. To determine the isolated effects of these alleles on different strain backgrounds, we produced the reciprocal congenic strains B6.CBACa-Cdh23(Ahl)(+) and CBACa.B6-Cdh23(ahl) and tested 15-30 mice from each for hearing loss progression. ABR thresholds for 8 kHz, 16 kHz, and 32 kHz pure-tone stimuli were measured at 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 and 18 months of age and compared with age-matched mice of the C57BL/6J and CBA/CaJ parental strains. Mice of the C57BL/6N strain, which is the source of embryonic stem cells for the large International Knockout Mouse Consortium, were also tested for comparisons with C57BL/6J mice. Mice of the C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N strains exhibited identical hearing loss profiles: their 32 kHz ABR thresholds were significantly higher than those of CBA/CaJ and congenic strain mice by 6 months of age, and their 16 kHz thresholds were significantly higher by 12 months. Thresholds of the CBA/CaJ, the B6.CBACa-Cdh23(Ahl)(+), and the CBACa.B6-Cdh23(ahl) strain mice differed little from one another and only slightly increased throughout the 18-month test period. Hearing loss, which corresponded well with cochlear hair cell loss, was most profound in the C57BL/6J and C57BL/6NJ strains. These results indicate that the CBA/CaJ-derived Cdh23(Ahl)(+) allele dramatically lessens hearing loss and hair cell death in an otherwise C57BL/6J genetic background, but that the C57BL/6J-derived Cdh23(ahl) allele has little effect on hearing loss in an otherwise CBA/CaJ background. We conclude that although Cdh23(ahl) homozygosity is necessary, it is not by itself sufficient to account for the accelerated hearing loss of C57BL/6J mice.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Cdh23 single nucleotide substitutions on age-related hearing loss in C57BL/6 and 129S1/Sv mice and comparisons with congenic strains.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 13;7:44450. doi: 10.1038/srep44450. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28287619 Free PMC article.
-
Separate and combined effects of Sod1 and Cdh23 mutations on age-related hearing loss and cochlear pathology in C57BL/6J mice.Hear Res. 2010 Sep 1;268(1-2):85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 May 12. Hear Res. 2010. PMID: 20470874 Free PMC article.
-
c.753A>G genome editing of a Cdh23ahl allele delays age-related hearing loss and degeneration of cochlear hair cells in C57BL/6J mice.Hear Res. 2020 Apr;389:107926. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2020.107926. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Hear Res. 2020. PMID: 32101784
-
Genetic influences on susceptibility of the auditory system to aging and environmental factors.Scand Audiol Suppl. 1992;36:1-39. Scand Audiol Suppl. 1992. PMID: 1488615 Review.
-
C57BL/6-derived mice and the Cdh23ahl allele - Background matters.Hear Res. 2025 Jun;462:109278. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2025.109278. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Hear Res. 2025. PMID: 40305983 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Mouse Models to Research in Hearing and Balance.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2016 Dec;17(6):493-523. doi: 10.1007/s10162-016-0589-1. Epub 2016 Oct 17. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 27752925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of CDH23 as a Significant Contributor to Progressive Postlingual Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Koreans.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 28;11(10):e0165680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165680. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27792758 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic projections of the subparafascicular thalamic nucleus to the auditory brainstem.Hear Res. 2016 Nov;341:202-209. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 27620513 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Oral Allylnitrile Administration on Cochlear Functioning in Mice Following Comparison of Different Anesthetics for Hearing Assessment.Front Toxicol. 2021 Feb 25;3:641569. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2021.641569. eCollection 2021. Front Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 35295154 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of a nuclear factor-kappa B-interacting immune gene network in mice cochleae with age-related hearing loss.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 22;16(10):e0258977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258977. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34679122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalton DS, Cruickshanks KJ, Klein BE, Klein R, Wiley TL, Nondahl DM. The impact of hearing loss on quality of life in older adults. Gerontologist. 2003;43:661–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

