Human FcγRIIA induces anaphylactic and allergic reactions
- PMID: 22138510
- PMCID: PMC3311274
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-07-367334
Human FcγRIIA induces anaphylactic and allergic reactions
Abstract
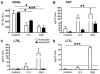
IgE and IgE receptors (FcεRI) are well-known inducers of allergy. We recently found in mice that active systemic anaphylaxis depends on IgG and IgG receptors (FcγRIIIA and FcγRIV) expressed by neutrophils, rather than on IgE and FcεRI expressed by mast cells and basophils. In humans, neutrophils, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils do not express FcγRIIIA or FcγRIV, but FcγRIIA. We therefore investigated the possible role of FcγRIIA in allergy by generating novel FcγRIIA-transgenic mice, in which various models of allergic reactions induced by IgG could be studied. In mice, FcγRIIA was sufficient to trigger active and passive anaphylaxis, and airway inflammation in vivo. Blocking FcγRIIA in vivo abolished these reactions. We identified mast cells to be responsible for FcγRIIA-dependent passive cutaneous anaphylaxis, and monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils to be responsible for FcγRIIA-dependent passive systemic anaphylaxis. Supporting these findings, human mast cells, monocytes and neutrophils produced anaphylactogenic mediators after FcγRIIA engagement. IgG and FcγRIIA may therefore contribute to allergic and anaphylactic reactions in humans.
Figures


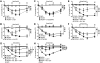

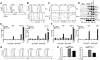

Comment in
-
Human FcγRIIA at center stage.Blood. 2012 Mar 15;119(11):2432-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-397786. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22422810 No abstract available.
References
-
- Daëron M. Fc receptor biology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:203–234. - PubMed
-
- Wershil BK, Mekori YA, Murakami T, Galli SJ. 125I-fibrin deposition in IgE-dependent immediate hypersensitivity reactions in mouse skin. Demonstration of the role of mast cells using genetically mast cell-deficient mice locally reconstituted with cultured mast cells. J Immunol. 1987;139(8):2605–2614. - PubMed
-
- Arimura A, Nagata M, Takeuchi M, Watanabe A, Nakamura K, Harada M. Active and passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in WBB6F1 mouse, a mast cell-deficient strain. Immunol Invest. 1990;19(3):227–233. - PubMed
-
- Arimura A, Nagata M, Watanabe A, Nakamura K, Takeuchi M, Harada M. Production of active and passive anaphylactic shock in the WBB6F1 mouse, a mast cell-deficient strain. Experientia. 1990;46(7):739–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

