Dnmt3a is essential for hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
- PMID: 22138693
- PMCID: PMC3637952
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1009
Dnmt3a is essential for hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
Abstract
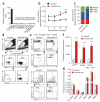
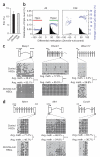
Loss of the de novo DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b in embryonic stem cells obstructs differentiation; however, the role of these enzymes in somatic stem cells is largely unknown. Using conditional ablation, we show that Dnmt3a loss progressively impairs hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) differentiation over serial transplantation, while simultaneously expanding HSC numbers in the bone marrow. Dnmt3a-null HSCs show both increased and decreased methylation at distinct loci, including substantial CpG island hypermethylation. Dnmt3a-null HSCs upregulate HSC multipotency genes and downregulate differentiation factors, and their progeny exhibit global hypomethylation and incomplete repression of HSC-specific genes. These data establish Dnmt3a as a critical participant in the epigenetic silencing of HSC regulatory genes, thereby enabling efficient differentiation.
Figures


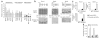
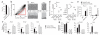

References
-
- Okano M, Xie S, Li E. Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat. Genet. 1998;19:219–220. - PubMed
-
- Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E. DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell. 1999;99:247–257. - PubMed
-
- Lei H, et al. De novo DNA cytosine methyltransferase activities in mouse embryonic stem cells. Development. 1996;122:3195–3205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- K99 DK084259-01A1/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA100632/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA100632/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL086223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK084259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL086223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK58192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 CA123344/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA129831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK084259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK092883/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

