EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NF-κB, interleukin-8 pathway
- PMID: 22139077
- PMCID: PMC3537826
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.563
EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NF-κB, interleukin-8 pathway
Abstract
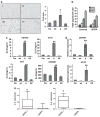
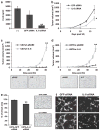
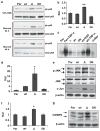
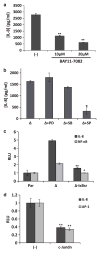
Sustaining a high growth rate requires tumors to exploit resources in their microenvironment. One example of this is the extensive angiogenesis that is a typical feature of high-grade gliomas. Here, we show that expression of the constitutively active mutant epidermal growth factor receptor, ΔEGFR (EGFRvIII, EGFR*, de2-7EGFR) is associated with significantly higher expression levels of the pro-angiogenic factor interleukin (IL)-8 in human glioma specimens and glioma stem cells. Furthermore, the ectopic expression of ΔEGFR in different glioma cell lines caused up to 60-fold increases in the secretion of IL-8. Xenografts of these cells exhibit increased neovascularization, which is not elicited by cells overexpressing wild-type (wt)EGFR or ΔEGFR with an additional kinase domain mutation. Analysis of the regulation of IL-8 by site-directed mutagenesis of its promoter showed that ΔEGFR regulates its expression through the transcription factors nuclear factor (NF)-κB, activator protein 1 (AP-1) and CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP). Glioma cells overexpressing ΔEGFR showed constitutive activation and DNA binding of NF-κB, overexpression of c-Jun and activation of its upstream kinase c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and overexpression of C/EBPβ. Selective pharmacological or genetic targeting of the NF-κB or AP-1 pathways efficiently blocked promoter activity and secretion of IL-8. Moreover, RNA interference-mediated knock-down of either IL-8 or the NF-κB subunit p65, in ΔEGFR-expressing cells attenuated their ability to form tumors and to induce angiogenesis when injected subcutaneously into nude mice. On the contrary, the overexpression of IL-8 in glioma cells lacking ΔEGFR potently enhanced their tumorigenicity and produced highly vascularized tumors, suggesting the importance of this cytokine and its transcription regulators in promoting glioma angiogenesis and tumor growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Antonyak MA, Moscatello DK, Wong AJ. Constitutive activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:2817–2822. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–277. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft CC, Chen Z, Yeh J, Sunwoo JB, Yeh NT, Jackson S, et al. Effects of pharmacologic antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3K and MEK signal kinases on NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Int J Cancer. 2002;99:538–548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

