Role of ArlRS in autolysis in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
- PMID: 22139508
- PMCID: PMC3272946
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.06261-11
Role of ArlRS in autolysis in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains
Abstract
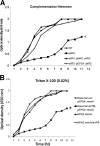
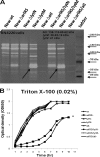
Autolysis plays an essential role in bacterial cell division and lysis with β-lactam antibiotics. Accordingly, the expression of autolysins is tightly regulated by several endogenous regulators, including ArlRS, a two component regulatory system that has been shown to negatively regulate autolysis in methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) strains. In this study, we found that inactivation of arlRS does not play a role in autolysis of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains, such as community-acquired (CA)-MRSA strains USA300 and MW2 or the hospital-acquired (HA)-MRSA strain COL. This contrasts with MSSA strains, including Newman, SH1000, RN6390, and 8325-4, where autolysis is affected by ArlRS. We further demonstrated that the striking difference in the roles of arlRS between MSSA and MRSA strains is not due to the methicillin resistance determinant mecA. Among known autolysins and their regulators, we found that arlRS represses lytN, while no effect was seen on atl, lytM, and lytH expression in both CA- and HA-MRSA strains. Transcriptional-fusion assays showed that the agr transcripts, RNAII and RNAIII, were significantly more downregulated in the arlRS mutant of MW2 than the MSSA strain Newman. Importantly, provision of agr RNAIII in trans to the MW2 arlRS mutant via a multicopy plasmid induced autolysis in this MRSA strain. Also, the autolytic phenotype in the arlRS mutant of MSSA strain Newman could be rescued by a mutation in either atl or lytM. Together, these data showed that ArlRS impacts autolysis differently in MSSA and MRSA strains.
Figures


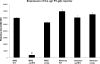

Similar articles
-
Role of mgrA and sarA in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus autolysis and resistance to cell wall-active antibiotics.J Infect Dis. 2009 Jan 15;199(2):209-18. doi: 10.1086/595740. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19072553 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus PBP4 is essential for beta-lactam resistance in community-acquired methicillin-resistant strains.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Nov;52(11):3955-66. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00049-08. Epub 2008 Aug 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18725435 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Generation Sequence Analysis Reveals Transfer of Methicillin Resistance to a Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Strain That Subsequently Caused a Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Outbreak: a Descriptive Study.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Sep;55(9):2808-2816. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00459-17. Epub 2017 Jul 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28679522 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in MRSA and MSSA Isolated from Clinical Samples in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Sep;26(9):1071-1080. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0001. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32159447
-
Methicillin/Oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a hospital and public health threat in Brazil.Braz J Infect Dis. 2010 Jan-Feb;14(1):71-6. doi: 10.1590/s1413-86702010000100014. Braz J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20428658 Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to complestatin and corbomycin depends on the VraSR two-component system.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 30;11(5):e0037023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00370-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37646518 Free PMC article.
-
Altering gene expression by aminocoumarins: the role of DNA supercoiling in Staphylococcus aureus.BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 16;15:291. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-291. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24734910 Free PMC article.
-
The ArlRS two-component system is a regulator of Staphylococcus aureus-induced endothelial cell damage.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Feb;37(2):289-292. doi: 10.1007/s10096-017-3130-5. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29177635
-
The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system regulates virulence factor expression through MgrA.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Jan;113(1):103-122. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14404. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31618469 Free PMC article.
-
The Staphylococcus aureus ArlRS two-component system is a novel regulator of agglutination and pathogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(12):e1003819. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003819. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24367264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baba T, et al. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819–1827 - PubMed
-
- Beier D, Gross R. 2006. Regulation of bacterial virulence by two-component systems. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9:143–152 - PubMed
-
- Boucher HW, Corey GR. 2008. Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46(Suppl. 5):S344–S349 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

