Global profiling of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in biological systems: high-throughput real-time analyses
- PMID: 22139901
- PMCID: PMC3270955
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.309062
Global profiling of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in biological systems: high-throughput real-time analyses
Abstract
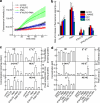
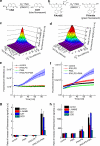
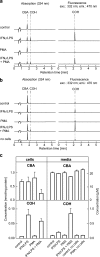
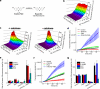
Herein we describe a high-throughput fluorescence and HPLC-based methodology for global profiling of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) in biological systems. The combined use of HPLC and fluorescence detection is key to successful implementation and validation of this methodology. Included here are methods to specifically detect and quantitate the products formed from interaction between the ROS/RNS species and the fluorogenic probes, as follows: superoxide using hydroethidine, peroxynitrite using boronate-based probes, nitric oxide-derived nitrosating species with 4,5-diaminofluorescein, and hydrogen peroxide and other oxidants using 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine (Amplex® Red) with and without horseradish peroxidase, respectively. In this study, we demonstrate real-time monitoring of ROS/RNS in activated macrophages using high-throughput fluorescence and HPLC methods. This global profiling approach, simultaneous detection of multiple ROS/RNS products of fluorescent probes, developed in this study will be useful in unraveling the complex role of ROS/RNS in redox regulation, cell signaling, and cellular oxidative processes and in high-throughput screening of anti-inflammatory antioxidants.
Figures



References
-
- Fruehauf J. P., Meyskens F. L., Jr. (2007) Reactive oxygen species: a breath of life or death? Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 789–794 - PubMed
-
- D'Autréaux B., Toledano M. B. (2007) ROS as signaling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 813–824 - PubMed
-
- Veal E. A., Day A. M., Morgan B. A. (2007) Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling. Mol. Cell 26, 1–14 - PubMed
-
- Rhee S. G. (2006) Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science 312, 1882–1883 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

