SitEx: a computer system for analysis of projections of protein functional sites on eukaryotic genes
- PMID: 22139920
- PMCID: PMC3245165
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr1187
SitEx: a computer system for analysis of projections of protein functional sites on eukaryotic genes
Abstract
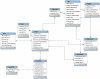
Search of interrelationships between the structural-functional protein organization and exon structure of encoding gene provides insights into issues concerned with the function, origin and evolution of genes and proteins. The functions of proteins and their domains are defined mostly by functional sites. The relation of the exon-intron structure of the gene to the protein functional sites has been little studied. Development of resources containing data on projections of protein functional sites on eukaryotic genes is needed. We have developed SitEx, a database that contains information on functional site amino acid positions in the exon structure of encoding gene. SitEx is integrated with the BLAST and 3DExonScan programs. BLAST is used for searching sequence similarity between the query protein and polypeptides encoded by single exons stored in SitEx. The 3DExonScan program is used for searching for structural similarity of the given protein with these polypeptides using superimpositions. The developed computer system allows users to analyze the coding features of functional sites by taking into account the exon structure of the gene, to detect the exons involved in shuffling in protein evolution, also to design protein-engineering experiments. SitEx is accessible at http://www-bionet.sscc.ru/sitex/. Currently, it contains information about 9994 functional sites presented in 2021 proteins described in proteomes of 17 organisms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computer analysis of protein functional sites projection on exon structure of genes in Metazoa.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 13(Suppl 13):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S13-S2. Epub 2015 Dec 16. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26693737 Free PMC article.
-
SITEX 2.0: Projections of protein functional sites on eukaryotic genes. Extension with orthologous genes.J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2017 Apr;15(2):1650044. doi: 10.1142/S021972001650044X. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28110602
-
XdomView: protein domain and exon position visualization.Bioinformatics. 2003 Jan;19(1):159-60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/19.1.159. Bioinformatics. 2003. PMID: 12499310
-
Protein domains correlate strongly with exons in multiple eukaryotic genomes--evidence of exon shuffling?Trends Genet. 2004 Sep;20(9):399-403. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2004.06.013. Trends Genet. 2004. PMID: 15313546 Review.
-
Evolution of the intron-exon structure of eukaryotic genes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Dec;5(6):774-8. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80010-3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995. PMID: 8745076 Review.
Cited by
-
ExonVisualiser - application for visualization exon units in 2D and 3D protein structures.Bioinformation. 2012;8(25):1280-2. doi: 10.6026/97320630081280. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Bioinformation. 2012. PMID: 23275735 Free PMC article.
-
Pocket-based drug design: exploring pocket space.AAPS J. 2013 Jan;15(1):228-41. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9426-6. Epub 2012 Nov 22. AAPS J. 2013. PMID: 23180158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computer analysis of protein functional sites projection on exon structure of genes in Metazoa.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 13(Suppl 13):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S13-S2. Epub 2015 Dec 16. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26693737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Todd AE, Orengo CA, Thornton JM. Evolution of function in protein superfamilies, from a structural perspective. J. Mol. Biol. 2001;307:1113–1143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

