The epigenome in early vertebrate development
- PMID: 22139962
- PMCID: PMC3294079
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.20831
The epigenome in early vertebrate development
Abstract
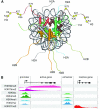
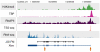
Epigenetic regulation defines the commitment and potential of cells, including the limitations in their competence to respond to inducing signals. This review discusses the developmental origins of chromatin state in Xenopus and other vertebrate species and provides an overview of its use in genome annotation. In most metazoans the embryonic genome is transcriptionally quiescent after fertilization. This involves nucleosome-dense chromatin, repressors and a temporal deficiency in the transcription machinery. Active histone modifications such as H3K4me3 appear in pluripotent blastula embryos, whereas repressive marks such as H3K27me3 show a major increase in enrichment during late blastula and gastrula stages. The H3K27me3 modification set by Polycomb restricts ectopic lineage-specific gene expression. Pluripotent chromatin in Xenopus embryos is relatively unconstrained, whereas the pluripotent cell lineage in mammalian embryos harbors a more enforced type of pluripotent chromatin.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

