Associations among parenting experiences during childhood and adolescence, hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis hypoactivity, and hippocampal gray matter volume reduction in young adults
- PMID: 22140014
- PMCID: PMC6870323
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21354
Associations among parenting experiences during childhood and adolescence, hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis hypoactivity, and hippocampal gray matter volume reduction in young adults
Abstract
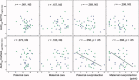
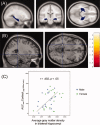
Recent human studies have indicated that adverse parenting experiences during childhood and adolescence are associated with adulthood hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis hypoactivity. Chronic HPA axis hypoactivity inhibits hippocampal gray matter (GM) development, as shown by animal studies. However, associations among adverse parenting experiences during childhood and adolescence, HPA axis activity, and brain development, particularly hippocampal development, are insufficiently investigated in humans. In this voxel-based structural magnetic resonance imaging study, using a cross-sectional design, we examined the associations among the scores of parental bonding instrument (PBI; a self-report scale to rate the attitudes of parents during the first 16 years), cortisol response determined by the dexamethasone/corticotropin-releasing hormone test, and regional or total hippocampal GM volume in forty healthy young adults with the following features: aged between 18 and 35 years, no cortisol hypersecretion in response to the dexamethasone test, no history of traumatic events, or no past or current conditions of significant medical illness or neuropsychiatric disorders. As a result, parental overprotection scores significantly negatively correlated with cortisol response. Additionally, a significant positive association was found between cortisol response and total or regional hippocampal GM volume. No significant association was observed between PBI scores and total or regional hippocampal GM volume. In conclusion, statistical associations were found between parental overprotection during childhood and adolescence and adulthood HPA axis hypoactivity, and between HPA axis hypoactivity and hippocampal GM volume reduction in healthy young adults, but no significant relationship was observed between any PBI scores and adulthood hippocampal GM volume.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term effects of early parental loss due to divorce on the HPA axis.Horm Behav. 2007 Apr;51(4):516-23. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2007.01.009. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Horm Behav. 2007. PMID: 17383654
-
Basal hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and corticotropin feedback in young and older men: relationships to magnetic resonance imaging-derived hippocampus and cingulate gyrus volumes.Neuroendocrinology. 2002 Apr;75(4):241-9. doi: 10.1159/000054715. Neuroendocrinology. 2002. PMID: 11979054 Clinical Trial.
-
Childhood parental loss and adult hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function.Biol Psychiatry. 2008 Jun 15;63(12):1147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Mar 12. Biol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18339361 Free PMC article.
-
Biology of posttraumatic stress disorder.J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 Suppl 17:41-6. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11495096 Review.
-
Early care experiences and HPA axis regulation in children: a mechanism for later trauma vulnerability.Prog Brain Res. 2008;167:137-49. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(07)67010-1. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18037012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lasting effects of stress physiology on the brain: Cortisol reactivity during preschool predicts hippocampal functional connectivity at school age.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019 Dec;40:100736. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100736. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31770714 Free PMC article.
-
Cortisol administration increases hippocampal activation to infant crying in males depending on childhood neglect.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Oct;35(10):5116-26. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22537. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 24757127 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal sensitivity, infant limbic structure volume and functional connectivity: a preliminary study.Transl Psychiatry. 2015 Oct 27;5(10):e668. doi: 10.1038/tp.2015.133. Transl Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26506054 Free PMC article.
-
Early-life experience, epigenetics, and the developing brain.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jan;40(1):141-53. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.140. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 24917200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, rationale and feasibility of a multidimensional experimental protocol to study early life stress.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2017 May 6;7:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2017.05.003. eCollection 2017 Sep. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2017. PMID: 29696166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aihara M, Ida I, Yuuki N, Oshima A, Kumano H, Takahashi K, Fukuda M, Oriuchi N, Endo K, Matsuda H, Mikuni M ( 2007): HPA axis dysfunction in unmedicated major depressive disorder and its normalization by pharmacotherapy correlates with alteration of neural activity in prefrontal cortex and limbic/paralimbic regions. Psychiatry Res 155: 245–256. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston K ( 2000): Voxel‐based morphometry—The methods. Neuroimage 11: 805–821. - PubMed
-
- Brand A, Richter‐Landsberg C, Leibfritz D ( 1993): Multinuclear NMR studies on the energy metabolism of glial and neuronal cells. Dev Neurosci 15: 289–298. - PubMed
-
- Bremner JD, Vythilingam M, Vermetten E, Southwick SM, McGlashan T, Nazeer A, Khan S, Vaccarino LV, Soufer R, Garg PK, Ng CK, Staib LH, Duncan JS, Charney DS ( 2003): MRI and PET study of deficits in hippocampal structure and function in women with childhood sexual abuse and posttraumatic stress disorder. Am J Psychiatry 160: 924–932. - PubMed
-
- Brett M, Anton J, Valabregue R, Poline J ( 2002): Region of interest analysis using an SPM toolbox [abstract]. Paper presented at the Eighth International Conference on Functional Mapping of the Human Brain, Sendai, Japan.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

