The structure and selectivity of the SR protein SRSF2 RRM domain with RNA
- PMID: 22140111
- PMCID: PMC3326313
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr1164
The structure and selectivity of the SR protein SRSF2 RRM domain with RNA
Abstract
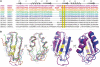
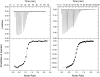
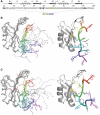
SRSF2 is a prototypical SR protein which plays important roles in the alternative splicing of pre-mRNA. It has been shown to be involved in regulatory pathways for maintaining genomic stability and play important roles in regulating key receptors in the heart. We report here the solution structure of the RNA recognition motifs (RRM) domain of free human SRSF2 (residues 9-101). Compared with other members of the SR protein family, SRSF2 structure has a longer L3 loop region. The conserved aromatic residue in the RNP2 motif is absent in SRSF2. Calorimetric titration shows that the RNA sequence 5'AGCAGAGUA3' binds SRSF2 with a K(d) of 61 ± 1 nM and a 1:1 stoichiometry. NMR and mutagenesis experiments reveal that for SFSF2, the canonical β1 and β3 interactions are themselves not sufficient for effective RNA binding; the additional loop L3 is crucial for RNA complex formation. A comparison is made between the structures of SRSF2-RNA complex with other known RNA complexes of SR proteins. We conclude that interactions involving the L3 loop, N- and C-termini of the RRM domain are collectively important for determining selectivity between the protein and RNA.
Figures

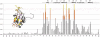
References
-
- Maris C, Dominguez C, Allain FH-T. The RNA recognition motif, a plastic RNA-binding platform to regulate post-transcriptional gene expression. FEBS J. 2005;272:2118–2131. - PubMed
-
- Bourgeois CF, Lejeune F, Stevenin J. Broad specificity of SR (serine/arginine) proteins in the regulation of alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNA. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2004;78:37–88. - PubMed
-
- Shen H, Kan JLC, Green MR. Arginine–serine-rich domains bound at splicing enhancers contact the branchpoint to promote prespliceosome assembly. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:367–376. - PubMed
-
- Wang HY, Xu X, Ding JH, Bermingham JR, Jr, Fu XD. SC35 plays a role in T cell development and alternative splicing of CD45. Mol. Cell. 2001;7:331–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

