The Polo-like kinase PLKA in Aspergillus nidulans is not essential but plays important roles during vegetative growth and development
- PMID: 22140227
- PMCID: PMC3272891
- DOI: 10.1128/EC.05130-11
The Polo-like kinase PLKA in Aspergillus nidulans is not essential but plays important roles during vegetative growth and development
Abstract
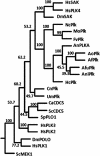
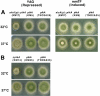
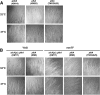
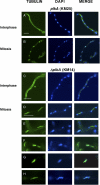
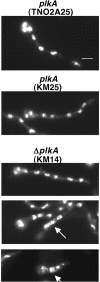
The Polo-like kinases (Plks) are conserved, multifunctional cell cycle regulators that are induced in many forms of cancer and play additional roles in metazoan development. We previously identified plkA in Aspergillus nidulans, the only Plk investigated in filamentous fungi to date, and partially characterized its function through overexpression. Here, we report the plkA null phenotype. Surprisingly, plkA was not essential, unlike Plks in other organisms that contain a single homologue. A subset of cells lacking PLKA contained defects in spindle formation and chromosome organization, supporting some conservation in cell cycle function. However, septa were present, suggesting that PLKA, unlike other Plks, is not a central regulator of septation. Colonies lacking PLKA were compact with multibranched hyphae, implying a role for this factor in aspects of hyphal morphogenesis. These defects were suppressed by high temperature or low concentrations of benomyl, suggesting that PLKA may function during vegetative growth by influencing microtubule dynamics. However, the colonies also showed reduced conidiation and precocious formation of sexual Hülle cells in a benomyl- and temperature-insensitive manner. This result suggests that PLKA may influence reproduction through distinct mechanisms and represents the first example of a link between Plk function and development in fungi. Finally, filamentous fungal Plks have distinct features, and phylogenetic analyses reveal that they may group more closely with metazoan PLK4. In contrast, yeast Plks are more similar to metazoan proteins PLK1 to PLK3. Thus, A. nidulans PLKA shows some conservation in cell cycle function but may also play novel roles during hyphal morphogenesis and development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The polo-like kinase PLKA is required for initiation and progression through mitosis in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jan;55(2):572-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04404.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15659171
-
The role of Aspergillus nidulans polo-like kinase PlkA in microtubule-organizing center control.J Cell Sci. 2021 Aug 15;134(16):jcs256537. doi: 10.1242/jcs.256537. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34328180
-
The pkaB gene encoding the secondary protein kinase A catalytic subunit has a synthetic lethal interaction with pkaA and plays overlapping and opposite roles in Aspergillus nidulans.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Aug;4(8):1465-76. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.8.1465-1476.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 16087751 Free PMC article.
-
Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188467. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33171265 Review.
-
Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;10(4):265-75. doi: 10.1038/nrm2653. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19305416 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional analysis of the Aspergillus nidulans kinome.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058008. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505451 Free PMC article.
-
Mannitol-1-phosphate dehydrogenase, MpdA, is required for mannitol production in vegetative cells and involved in hyphal branching, heat resistance of conidia and sexual development in Aspergillus nidulans.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):613-630. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01163-6. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33683401
-
Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits ParA and PabA orchestrate septation and conidiation and are essential for PP2A activity in Aspergillus nidulans.Eukaryot Cell. 2014 Dec;13(12):1494-506. doi: 10.1128/EC.00201-14. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Eukaryot Cell. 2014. PMID: 25280816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams TH, Boylan MT, Timberlake WE. 1988. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 54:353–362 - PubMed
-
- Alexandru G, Uhlmann F, Mechtler K, Poupart MA, Nasmyth K. 2001. Phosphorylation of the cohesin subunit Scc1 by Polo/Cdc5 kinase regulates sister chromatid separation in yeast. Cell 105:459–472 - PubMed
-
- Archambault V, Glover DM. 2009. Polo-like kinases: conservation and divergence in their functions and regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:265–275 - PubMed
-
- Bachewich C, Masker K, Osmani S. 2005. The polo-like kinase PLKA is required for initiation and progression through mitosis in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 55:572–587 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

