Constructing a population-based research database from routine maternal screening records: a resource for studying alloimmunization in pregnant women
- PMID: 22140452
- PMCID: PMC3227597
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027619
Constructing a population-based research database from routine maternal screening records: a resource for studying alloimmunization in pregnant women
Abstract
Background: Although screening for maternal red blood cell antibodies during pregnancy is a standard procedure, the prevalence and clinical consequences of non-anti-D immunization are poorly understood. The objective was to create a national database of maternal antibody screening results that can be linked with population health registers to create a research resource for investigating these issues.
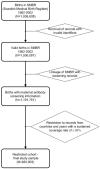
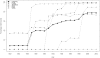
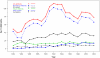
Study design and methods: Each birth in the Swedish Medical Birth Register was uniquely identified and linked to the text stored in routine maternal antibody screening records in the time window from 9 months prior to 2 weeks after the delivery date. These text records were subjected to a computerized search for specific antibodies using regular expressions. To illustrate the research potential of the resulting database, selected antibody prevalence rates are presented as tables and figures, and the complete data (from more than 60 specific antibodies) presented as online moving graphical displays.
Results: More than one million (1,191,761) births with valid screening information from 1982-2002 constitute the study population. Computerized coverage of screening increased steadily over time and varied by region as electronic records were adopted. To ensure data quality, we restricted analysis to birth records in areas and years with a sustained coverage of at least 80%, representing 920,903 births from 572,626 mothers in 17 of the 24 counties in Sweden. During the study period, non-anti-D and anti-D antibodies occurred in 76.8/10,000 and 14.1/10,000 pregnancies respectively, with marked differences between specific antibodies over time.
Conclusion: This work demonstrates the feasibility of creating a nationally representative research database from the routine maternal antibody screening records from an extended calendar period. By linkage with population registers of maternal and child health, such data are a valuable resource for addressing important clinical questions, such as the etiological significance of non-anti-D antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of Rhesus and non-Rhesus maternal red blood cell alloimmunization with stillbirth and preterm birth.Int J Epidemiol. 2014 Aug;43(4):1123-31. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyu079. Epub 2014 May 5. Int J Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24801308 Free PMC article.
-
[Spontaneous antepartal RhD alloimmunization].Ceska Gynekol. 2015 Dec;80(6):401-4. Ceska Gynekol. 2015. PMID: 26741153 Czech.
-
Prevention of Rh alloimmunization.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2003 Sep;25(9):765-73. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(16)31006-4. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2003. PMID: 12970812
-
RhD isoimmunization and current management modalities.J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2001 Nov-Dec;30(6):589-606. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2001.tb00006.x. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2001. PMID: 11724195 Review.
-
Approach to red blood cell antibody testing during pregnancy: Answers to commonly asked questions.Can Fam Physician. 2020 Jul;66(7):491-498. Can Fam Physician. 2020. PMID: 32675093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suicidality in Chronic Illness: An Overview of Cognitive-Affective and Interpersonal Factors.J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2021 Mar;28(1):137-148. doi: 10.1007/s10880-020-09749-x. Epub 2020 Oct 31. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2021. PMID: 33128664 Review.
-
Associations of Rhesus and non-Rhesus maternal red blood cell alloimmunization with stillbirth and preterm birth.Int J Epidemiol. 2014 Aug;43(4):1123-31. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyu079. Epub 2014 May 5. Int J Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24801308 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn within a Large Integrated Health Care System.Am J Perinatol. 2025 May;42(7):924-932. doi: 10.1055/a-2444-2314. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Am J Perinatol. 2025. PMID: 39532115 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted routine antenatal anti-D prophylaxis in the prevention of RhD immunisation--outcome of a new antenatal screening and prevention program.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 6;8(8):e70984. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070984. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23940682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Urbaniak SJ, Greiss MA. RhD haemolytic disease of the fetus and the newborn. Blood Rev. 2000;14:44–61. - PubMed
-
- Daniels G. Blood group antibodies in haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. In: Hadley A, Soothill P, editors. Alloimmune disorders of pregnancy. Cambridge University Press; 2002. pp. 21–40.
-
- Engelfriet CP, Reesink HW, Judd WJ, Ulander VM, Kuosmanen M, et al. Current status of immunoprophylaxis with anti-D immunoglobin. Vox Sang. 2003;85:328–37. - PubMed
-
- Moise KJ. Fetal anemia due to non-Rhesus-D red-cell alloimmunization. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2008;13:207–14. - PubMed
-
- Bowell PJ, Allen DL, Entwistle CC. Blood group antibody screening tests during pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1986;93:1038–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

