A quantitative method for the specific assessment of caspase-6 activity in cell culture
- PMID: 22140457
- PMCID: PMC3226564
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027680
A quantitative method for the specific assessment of caspase-6 activity in cell culture
Abstract
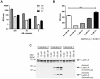
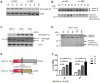
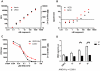
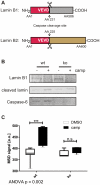
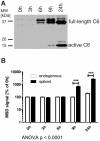
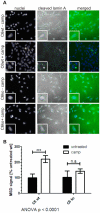
Aberrant activation of caspase-6 has recently emerged as a major contributor to the pathogeneses of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's and Huntington disease. Commercially available assays to measure caspase-6 activity commonly use the VEID peptide as a substrate. However these methods are not well suited to specifically assess caspase-6 activity in the presence of other, confounding protease activities, as often encountered in cell and tissue samples. Here we report the development of a method that overcomes this limitation by using a protein substrate, lamin A, which is highly specific for caspase-6 cleavage at amino acid 230. Using a neo-epitope antibody against cleaved lamin A, we developed an electrochemiluminescence-based ELISA assay that is suitable to specifically detect and quantify caspase-6 activity in highly apoptotic cell extracts. The method is more sensitive than VEID-based assays and can be adapted to a high-content imaging platform for high-throughput screening. This method should be useful to screen for and characterize caspase-6 inhibitor compounds and other interventions to decrease intracellular caspase-6 activity for applications in neurodegenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A whole cell assay to measure caspase-6 activity by detecting cleavage of lamin A/C.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030376. Epub 2012 Jan 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253931 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of lamin A by Mch2 alpha but not CPP32: multiple interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme-related proteases with distinct substrate recognition properties are active in apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8395-400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8395. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8710882 Free PMC article.
-
Activated caspase-6 and caspase-6-cleaved fragments of huntingtin specifically colocalize in the nucleus.Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Aug 1;17(15):2390-404. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn139. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Hum Mol Genet. 2008. PMID: 18445618
-
Activation and regulation of caspase-6 and its role in neurodegenerative diseases.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015;55:553-72. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124414. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25340928 Review.
-
Caspase-6 and neurodegeneration.Trends Neurosci. 2011 Dec;34(12):646-56. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.09.001. Epub 2011 Oct 22. Trends Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22018804 Review.
Cited by
-
A Huntingtin-based peptide inhibitor of caspase-6 provides protection from mutant Huntingtin-induced motor and behavioral deficits.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 May 1;24(9):2604-14. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv023. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 25616965 Free PMC article.
-
An AMPK-caspase-6 axis controls liver damage in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Science. 2020 Feb 7;367(6478):652-660. doi: 10.1126/science.aay0542. Science. 2020. PMID: 32029622 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of mutant huntingtin at serine 116 modulates neuronal toxicity.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 5;9(2):e88284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088284. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24505464 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the role of key amino acids in regulation of proline dehydrogenase/proline oxidase (prodh/pox)-dependent apoptosis/autophagy as an approach to targeted cancer therapy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Mar;466(1-2):35-44. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03685-y. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31933109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory role of cathepsin L in induction of nuclear laminopathy in Alzheimer's disease.Aging Cell. 2022 Jan;21(1):e13531. doi: 10.1111/acel.13531. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 34905652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feinstein-Rotkopf Y, Arama E. Can't live without them, can live with them: roles of caspases during vital cellular processes. Apoptosis. 2009;14:980–995. - PubMed
-
- Thornberry NA. Caspases: key mediators of apoptosis. Chem Biol. 1998;5:R97–103. - PubMed
-
- Talanian RV, Quinlan C, Trautz S, Hackett MC, Mankovich JA, et al. Substrate specificities of caspase family proteases. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:9677–9682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

