Alterations in the interleukin-1/interleukin-1 receptor antagonist balance modulate cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction in the mouse
- PMID: 22140485
- PMCID: PMC3225370
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027923
Alterations in the interleukin-1/interleukin-1 receptor antagonist balance modulate cardiac remodeling following myocardial infarction in the mouse
Abstract
Background: Healing after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is characterized by an intense inflammatory response and increased Interleukin-1 (IL-1) tissue activity. Genetically engineered mice lacking the IL-1 receptor (IL-1R1-/-, not responsive to IL-1) or the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra, enhanced response to IL-1) have an altered IL-1/IL-1Ra balance that we hypothesize modulates infarct healing and cardiac remodeling after AMI.
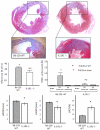
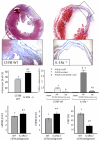
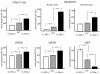
Methods: IL-1R1-/- and IL-1Ra-/- male mice and their correspondent wild-types (WT) were subjected to permanent coronary artery ligation or sham surgery. Infarct size (trichrome scar size), apoptotic cell death (TUNEL) and left ventricular (LV) dimensions and function (echocardiography) were measured prior to and 7 days after surgery.
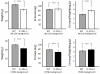
Results: When compared with the corresponding WT, IL-1R1-/- mice had significantly smaller infarcts (-25%), less cardiomyocyte apoptosis (-50%), and reduced LV enlargement (LV end-diastolic diameter increase [LVEDD], -20%) and dysfunction (LV ejection fraction [LVEF] decrease, -50%), whereas IL-1Ra-/- mice had significantly larger infarcts (+75%), more apoptosis (5-fold increase), and more severe LV enlargement (LVEDD increase,+30%) and dysfunction (LVEF decrease, +70%)(all P values <0.05).
Conclusions: An imbalance in IL-1/IL-1Ra signaling at the IL-1R1 level modulates the severity of cardiac remodeling after AMI in the mouse, with reduced IL-1R1 signaling providing protection and unopposed IL-1R1 signaling providing harm.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Labow M, Shuster D, Zetterstrom M, Nunes P, Terry R, et al. Absence of IL-1 signaling and reduced inflammatory response in IL-1 type I receptor-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1997;159:2452–2461. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP. The balance between IL-1 and IL-1Ra in disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:323–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

