Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling antagonizes serous ovarian cancer growth in a primary xenograft model
- PMID: 22140510
- PMCID: PMC3226669
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028077
Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling antagonizes serous ovarian cancer growth in a primary xenograft model
Abstract
Background: Recent evidence links aberrant activation of Hedgehog (Hh) signaling with the pathogenesis of several cancers including medulloblastoma, basal cell, small cell lung, pancreatic, prostate and ovarian. This investigation was designed to determine if inhibition of this pathway could inhibit serous ovarian cancer growth.
Methodology: We utilized an in vivo pre-clinical model of serous ovarian cancer to characterize the anti-tumor activity of Hh pathway inhibitors cyclopamine and a clinically applicable derivative, IPI-926. Primary human serous ovarian tumor tissue was used to generate tumor xenografts in mice that were subsequently treated with cyclopamine or IPI-926.
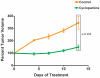
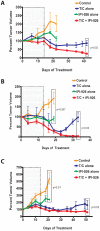
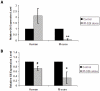
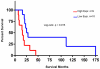
Principal findings: Both compounds demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity as single agents. When IPI-926 was used in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatinum (T/C), no synergistic effect was observed, though sustained treatment with IPI-926 after cessation of T/C continued to suppress tumor growth. Hh pathway activity was analyzed by RT-PCR to assess changes in Gli1 transcript levels. A single dose of IPI-926 inhibited mouse stromal Gli1 transcript levels at 24 hours with unchanged human intra-tumor Gli1 levels. Chronic IPI-926 therapy for 21 days, however, inhibited Hh signaling in both mouse stromal and human tumor cells. Expression data from the micro-dissected stroma in human serous ovarian tumors confirmed the presence of Gli1 transcript and a significant association between elevated Gli1 transcript levels and worsened survival.
Conclusions/significance: IPI-926 treatment inhibits serous tumor growth suggesting the Hh signaling pathway contributes to the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer and may hold promise as a novel therapeutic target, especially in the maintenance setting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 (gli1) in advanced serous ovarian cancer is associated with unfavorable overall survival.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060145. Epub 2013 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555905 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog pathway inhibition in chondrosarcoma using the smoothened inhibitor IPI-926 directly inhibits sarcoma cell growth.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 May;13(5):1259-69. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0731. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 24634412
-
Synergism between Hedgehog-GLI and EGFR signaling in Hedgehog-responsive human medulloblastoma cells induces downregulation of canonical Hedgehog-target genes and stabilized expression of GLI1.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 10;8(6):e65403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065403. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762360 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Signaling and Truncated GLI1 in Cancer.Cells. 2020 Sep 17;9(9):2114. doi: 10.3390/cells9092114. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32957513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of hedgehog/Gli signaling by botanicals: a review of compounds with potential hedgehog pathway inhibitory activities.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;13(5):580-95. doi: 10.2174/15680096113139990003. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013. PMID: 23675897 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety and Tolerability of Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors in Cancer.Drug Saf. 2019 Feb;42(2):263-279. doi: 10.1007/s40264-018-0777-5. Drug Saf. 2019. PMID: 30649745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of the tumor stroma in ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2014 May 13;4:104. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00104. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24860785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ovarian cancer stem cells or tumor-initiating cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 25;14(4):6624-48. doi: 10.3390/ijms14046624. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23528891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting HER2 in patient-derived xenograft ovarian cancer models sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy.Mol Oncol. 2019 Feb;13(2):132-152. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12414. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30499260 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog pathway for the treatment of inflammatory diseases: implications and opportunities for future research.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Jun;10(6):e004397. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004397. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35710292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Growdon WB, Birrer MJ, Penson RT. Ovarian Cancer: Individualized and Personalized Care. Expert Rev Obstet Gynecol. 2010;5:409–419.
-
- Ingham PW, McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001;15:3059–3087. - PubMed
-
- Taipale J, Beachy PA. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature. 2001;411:349–354. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, McMahon AP, Allen BL. Shifting paradigms in Hedgehog signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:159–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

