TRAF6 and IRF7 control HIV replication in macrophages
- PMID: 22140520
- PMCID: PMC3225375
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028125
TRAF6 and IRF7 control HIV replication in macrophages
Abstract
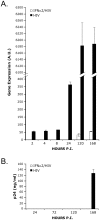
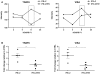
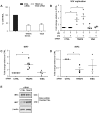
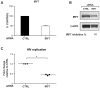
The innate immune system recognizes virus infection and evokes antiviral responses which include producing type I interferons (IFNs). The induction of IFN provides a crucial mechanism of antiviral defense by upregulating interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) that restrict viral replication. ISGs inhibit the replication of many viruses by acting at different steps of their viral cycle. Specifically, IFN treatment prior to in vitro human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection stops or significantly delays HIV-1 production indicating that potent inhibitory factors are generated. We report that HIV-1 infection of primary human macrophages decreases tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and virus-induced signaling adaptor (VISA) expression, which are both components of the IFN signaling pathway controlling viral replication. Knocking down the expression of TRAF6 in macrophages increased HIV-1 replication and augmented the expression of IRF7 but not IRF3. Suppressing VISA had no impact on viral replication. Overexpression of IRF7 resulted in enhanced viral replication while knocking down IRF7 expression in macrophages significantly reduced viral output. These findings are the first demonstration that TRAF6 can regulate HIV-1 production and furthermore that expression of IRF7 promotes HIV-1 replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of Interferon-Stimulated Gene Induction in HIV-1-Infected Macrophages.J Virol. 2017 Sep 27;91(20):e00744-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00744-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28768867 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6 establishes innate immune responses by activating NF-kappaB and IRF7 upon sensing cytosolic viral RNA and DNA.PLoS One. 2009 May 25;4(5):e5674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005674. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19479062 Free PMC article.
-
Immune activation of human brain microvascular endothelial cells inhibits HIV replication in macrophages.Blood. 2013 Apr 11;121(15):2934-42. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-08-450353. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23401273 Free PMC article.
-
VISA--a pass to innate immunity.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(2):287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.08.016. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17029998 Review.
-
Interferon-Regulated Expression of Cellular Splicing Factors Modulates Multiple Levels of HIV-1 Gene Expression and Replication.Viruses. 2024 Jun 11;16(6):938. doi: 10.3390/v16060938. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 Vpr induces interferon-stimulated genes in human monocyte-derived macrophages.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e106418. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106418. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25170834 Free PMC article.
-
A multi-trait epigenome-wide association study identified DNA methylation signature of inflammation among people with HIV.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 May 31:rs.3.rs-4419840. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4419840/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Nov 2;16(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01763-2. PMID: 38854093 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
HIV-Infected Macrophages Are Infected and Killed by the Interferon-Sensitive Rhabdovirus MG1.J Virol. 2021 Apr 12;95(9):e01953-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01953-20. Print 2021 Apr 12. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33568507 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6 and TAK1 Contribute to SAMHD1-Mediated Negative Regulation of NF-κB Signaling.J Virol. 2021 Jan 13;95(3):e01970-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01970-20. Print 2021 Jan 13. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33177202 Free PMC article.
-
Sirtuin 1-Chromatin-Binding Dynamics Points to a Common Mechanism Regulating Inflammatory Targets in SIV Infection and in the Aging Brain.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;13(2):163-178. doi: 10.1007/s11481-017-9772-3. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29280055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutler B, Hoebe K, Du X, Ulevitch RJ. How we detect microbes and respond to them: the Toll-like receptors and their transducers. J Leukoc Biol. 2003;74:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Takeda K, Akira S. Toll receptors and pathogen resistance. Cell Microbiol. 2003;5:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Meylan PR, Guatelli JC, Munis JR, Richman DD, Kornbluth RS. Mechanisms for the inhibition of HIV replication by interferons-alpha, -beta, and -gamma in primary human macrophages. Virology. 1993;193:138–148. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Langer JA, Zoon KC, Samuel CE. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

