Diverse roles of Eph/ephrin signaling in the mouse lens
- PMID: 22140528
- PMCID: PMC3226676
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028147
Diverse roles of Eph/ephrin signaling in the mouse lens
Abstract
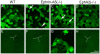
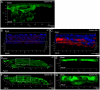
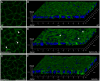
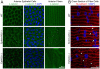
Recent genetic studies show that the Eph/ephrin bidirectional signaling pathway is associated with both congenital and age-related cataracts in mice and humans. We have investigated the molecular mechanisms of cataractogenesis and the roles of ephrin-A5 and EphA2 in the lens. Ephrin-A5 knockout ⁻/⁻ mice often display anterior polar cataracts while EphA2⁻/⁻ lenses show very mild cortical or nuclear cataracts at weaning age. The anterior polar cataract of ephrin-A5⁻/⁻ lenses is correlated with multilayers of aberrant cells that express alpha smooth muscle actin, a marker for mesenchymal cells. Only select fiber cells are altered in ephrin-A5⁻/⁻ lenses. Moreover, the disruption of membrane-associated β-catenin and E-cadherin junctions is observed in ephrin-A5⁻/⁻ lens central epithelial cells. In contrast, EphA2⁻/⁻ lenses display normal monolayer epithelium while disorganization is apparent in all lens fiber cells. Immunostaining of ephrin-A5 proteins, highly expressed in lens epithelial cells, were not colocalized with EphA2 proteins, mainly expressed in lens fiber cells. Besides the previously reported function of ephrin-A5 in lens fiber cells, this work suggests that ephrin-A5 regulates β-catenin signaling and E-cadherin to prevent lens anterior epithelial cells from undergoing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition while EphA2 is essential for controlling the organization of lens fiber cells through an unknown mechanism. Ephrin-A5 and EphA2 likely interacting with other members of Eph/ephrin family to play diverse functions in lens epithelial cells and/or fiber cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Yamamoto N, Majima K, Marunouchi T. A study of the proliferating activity in lens epithelium and the identification of tissue-type stem cells. Med Mol Morphol. 2008;41:83–91. - PubMed
-
- Piatigorsky J. Lens differentiation in vertebrates. A review of cellular and molecular features. Differentiation. 1981;19:134–153. - PubMed
-
- Zampighi GA, Eskandari S, Kreman M. Epithelial organization of the mammalian lens. Exp Eye Res. 2000;71:415–435. - PubMed
-
- Kuszak JR, Novak LA, Brown HG. An ultrastructural analysis of the epithelial-fiber interface (EFI) in primate lenses. Exp Eye Res. 1995;61:579–597. - PubMed
-
- Bassnett S, Winzenburger PA. Morphometric analysis of fibre cell growth in the developing chicken lens. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76:291–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

