Clonal replacement of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in a German university hospital over a period of eleven years
- PMID: 22140542
- PMCID: PMC3227659
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028189
Clonal replacement of epidemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains in a German university hospital over a period of eleven years
Abstract
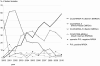
Worldwide, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pose an increased risk for healthcare- and community-associated infections. Since the first report of MRSA in England in 1961, several distinct clones or strains have emerged. Changes within the MRSA population of whole countries, small regions or of single hospitals have been observed with some clones replacing others. In this study, the clonal replacement of MRSA isolates in a South-eastern German tertiary care hospital between 2000 and 2010 is described based on microarray analyses of 778 isolates and at least 50 MRSA per year. Within these eleven years, four common epidemic strains, CC22-MRSA-IV, CC45-MRSA-IV, CC5/ST228-MRSA-I (including a variant with a truncated SCCmec element) and CC5-MRSA-II were identified. The PVL-negative CC22-MRSA-IV strain (Barnim Epidemic Strain, UK-EMRSA-15) was detected for the first time in 2001 and its abundance increased since then to 58.6% in 2010. CC5-MRSA-II increased from 2% (2000) to about 30% (2003), and since then it fluctuates between 23 and 37% of isolates. CC5/ST228-MRSA-I decreased from about the half of tested isolates (2000) to 2.3% (2010). A similar trend was observed for CC45-MRSA-IV, which decreased drastically down to 3.4% in 2010 after reaching a maximum of 62.0% in 2002. Seventeen other PVL-negative MRSA strains were identified sporadically with no significant trend being observed. Seven PVL-positive MRSA strains were found, but they remained rare during the study period accounting together for 2.7% of isolates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Jevons MP. “Celbenin”-resistant Staphylococci. British Medical Journal. 1961;1:1924–1925.
-
- Hiramatsu K, Cui L, Kuroda M, Ito T. The emergence and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Trends in Microbiology. 2001;9:486–493. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases