Ethanol exposure during pregnancy persistently attenuates cranially directed blood flow in the developing fetus: evidence from ultrasound imaging in a murine second trimester equivalent model
- PMID: 22141380
- PMCID: PMC3297711
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01676.x
Ethanol exposure during pregnancy persistently attenuates cranially directed blood flow in the developing fetus: evidence from ultrasound imaging in a murine second trimester equivalent model
Abstract
Background: Ethanol (EtOH) consumption during pregnancy can lead to fetal growth retardation, mental retardation, and neurodevelopmental delay. The fetal brain initiates neurogenesis and vasculogenesis during the second trimester, and depends on maternal-fetal circulation for nutrition and growth signals. We used high-resolution in vivo ultrasound imaging to test the hypothesis that EtOH interferes with fetal brain-directed blood flow during this critical developmental period.
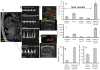
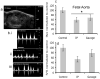
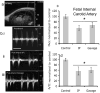
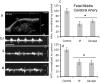
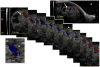
Methods: Pregnant mice were lightly anesthetized on gestational day 12 with an isoflurane/oxygen mixture. We assessed the effect of single and repeated binge-like maternal EtOH exposures at 3 g/kg, administered by intragastric gavage or intraperitoneal injection, on maternal circulation and fetal umbilical, aortic, internal carotid, and middle cerebral arterial circulation.
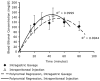
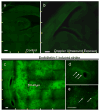
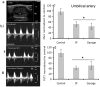
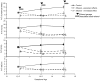
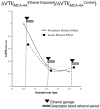
Results: Binge maternal EtOH exposure, regardless of exposure route, significantly reduced fetal arterial blood acceleration and velocity time integral (VTI), from umbilical to cerebral arteries, without a change in fetal heart rate and resistivity indices. Importantly a single maternal binge EtOH exposure induced persistent suppression of fetal arterial VTI for at least 24 hours. Repeated binge episodes resulted in a continuing and persistent suppression of fetal VTI. Qualitative assessments showed that maternal EtOH exposure induced oscillatory, nondirectional blood flow in fetal cerebral arteries. Maternal cardiac and other physiological parameters remained unaltered.
Conclusions: These data show that binge-type maternal EtOH exposure results in rapid and persistent loss of blood flow from the umbilical artery to the fetal brain, potentially compromising nutrition and the maternal/fetal endocrine environment during a critical period for neuron formation and angiogenesis in the maturing brain.
Copyright © 2011 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures

References
-
- Abel EL. Prenatal effects of alcohol. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1984;14(1):1–10. - PubMed
-
- Abel EL. An update on incidence of FAS: FAS is not an equal opportunity birth defect. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1995;17(4):437–43. - PubMed
-
- Bayer S, Altman J, Russo R, Zhang X. Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neuro Toxicology. 1993;14(1):83–144. - PubMed
-
- Bearer CF. L1 cell adhesion molecule signal cascades: targets for ethanol developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology. 2001;22(5):625–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

