Differential interference effects of negative emotional states on subsequent semantic and perceptual processing
- PMID: 22142207
- PMCID: PMC3342928
- DOI: 10.1037/a0026329
Differential interference effects of negative emotional states on subsequent semantic and perceptual processing
Abstract
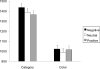
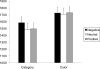
Past studies have revealed that encountering negative events interferes with cognitive processing of subsequent stimuli. The present study investigates whether negative events affect semantic and perceptual processing differently. Presentation of negative pictures produced slower reaction times than neutral or positive pictures in tasks that require semantic processing, such as natural or man-made judgments about drawings of objects, commonness judgments about objects, and categorical judgments about pairs of words. In contrast, negative picture presentation did not slow down judgments in subsequent perceptual processing (e.g., color judgments about words, size judgments about objects). The subjective arousal level of negative pictures did not modulate the interference effects on semantic or perceptual processing. These findings indicate that encountering negative emotional events interferes with semantic processing of subsequent stimuli more strongly than perceptual processing, and that not all types of subsequent cognitive processing are impaired by negative events.
(c) 2011 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures

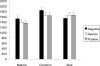
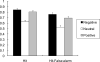

Similar articles
-
Prior perceptual processing enhances the effect of emotional arousal on the neural correlates of memory retrieval.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jul;112:104-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24380867 Free PMC article.
-
The costs of emotional attention: affective processing inhibits subsequent lexico-semantic analysis.J Cogn Neurosci. 2007 Dec;19(12):1932-49. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.12.1932. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17892390
-
Evaluative priming from subliminal emotional words: insights from event-related potentials and individual differences related to anxiety.Conscious Cogn. 2009 Jun;18(2):383-400. doi: 10.1016/j.concog.2009.02.007. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Conscious Cogn. 2009. PMID: 19328727
-
Positive and negative emotion enhances the processing of famous faces in a semantic judgment task.Neuropsychology. 2010 Jan;24(1):84-9. doi: 10.1037/a0017202. Neuropsychology. 2010. PMID: 20063949
-
Can automatic picture processing influence word judgments?J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 1982 Sep;8(5):418-34. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.8.5.418. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 1982. PMID: 6215463
Cited by
-
The neural correlates of context driven changes in the emotional response: An fMRI study.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 30;17(12):e0279823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279823. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36584048 Free PMC article.
-
Arousal-Biased Competition in Perception and Memory.Perspect Psychol Sci. 2011 Mar;6(2):114-33. doi: 10.1177/1745691611400234. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21660127 Free PMC article.
-
Mood effects on semantic processes: Behavioural and electrophysiological evidence.Front Psychol. 2022 Nov 11;13:1014706. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1014706. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36438367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of aging on emotion-induced modulations of source retrieval ERPs: evidence for valence biases.Neuropsychologia. 2012 Dec;50(14):3370-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.09.024. Epub 2012 Sep 24. Neuropsychologia. 2012. PMID: 23017596 Free PMC article.
-
Prior perceptual processing enhances the effect of emotional arousal on the neural correlates of memory retrieval.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Jul;112:104-13. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.12.012. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24380867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander JK, Hillier A, Smith RM, Tivarus ME, Beversdorf DQ. Beta-adrenergic modulation of cognitive flexibility during stress. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2007;19:468–478. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.3.468. - PubMed
-
- Anderson AK. Affective influences on the attentional dynamics supporting awareness. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General. 2005;134:258–281. doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.134.2.258. - PubMed
-
- Aquino JM, Arnell KM. Attention and the processing of emotional words: Dissociating effects of arousal. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review. 2007;14:430–435. - PubMed
-
- Arnell KM, Killman KV, Fijavz D. Blinded by emotion : Target misses follow attention capture by arousing distractors in rsvp. Emotion. 2007;7:465–477. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.3.465. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann T, Hommuk K. How backward masking becomes attentional blink. Psychological Science. 2005;16:740–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2005.01604.x. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

