Evaluation of the migraine treatment sumatriptan/naproxen sodium on blood pressure following long-term administration
- PMID: 22142350
- PMCID: PMC8108967
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00554.x
Evaluation of the migraine treatment sumatriptan/naproxen sodium on blood pressure following long-term administration
Abstract
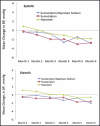
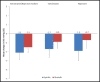
Anti-inflammatory and pain therapies have been associated with blood pressure (BP) destabilization. Hence, the effects on BP of sumatriptan/naproxen sodium in fixed-dose combination, sumatriptan 85 mg, and naproxen sodium 500 mg administered intermittently for the acute treatment of migraine attacks were assessed. Patients with migraine with or without aura and no history of hypertension were randomized to sumatriptan/naproxen sodium (n=135), sumatriptan (n=136), or naproxen sodium (n=136) to treat migraine attacks for 6 months in a double-blind, parallel-group trial. Following a treated migraine attack, patients performed 2 consecutive days of self-measured BPs beginning ≥24 hours after the last dose of study medication and transmitted them by a transtelephonic modem. The primary end point was the change from baseline in self-measured BP at 6 months. Changes in self-measured BP from baseline to 6 months for sumatriptan/naproxen sodium were -2.1/-1.5 mm Hg (95% confidence intervals, -3.4 to -0.8 for systolic and -2.6 to -0.3 for diastolic). Mean changes from baseline in self-measured BP did not differ among the 3 treatment groups. Additional categorical analyses did not show increases from baseline with sumatriptan/naproxen sodium relative to either of the monotherapy groups. Intermittent acute migraine treatment with sumatriptan/naproxen sodium for up to 6 months was associated with clinically insignificant decreases in self-measured BP that were similar to those with sumatriptan or naproxen alone in normotensive patients with migraine.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Cleves C, Tepper SJ. Sumatriptan/naproxen sodium combination for the treatment of migraine. Expert Rev Neurother. 2008;8:1289–1297. - PubMed
-
- Brandes JL, Kudrow D, Stark SR, et al. Sumatriptan‐naproxen for acute treatment of migraine. JAMA. 2007;297:1443–1454. - PubMed
-
- Winner P, Cady RK, Ruoff GE, et al. Twelve‐month tolerability and safety of sumatriptan‐naproxen sodium for the treatment of acute migraine. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82:61–68. - PubMed
-
- Fowler PA, Lacey LF, Thomas M, et al. The clinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sumatriptan. Eur Neurol. 1991;31:291–294. - PubMed
-
- Imitrex (sumatriptan tablets) prescribing information. GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle Park, NC. February 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

