Trp2 peptide vaccine adjuvanted with (R)-DOTAP inhibits tumor growth in an advanced melanoma model
- PMID: 22142394
- PMCID: PMC3273554
- DOI: 10.1021/mp200350n
Trp2 peptide vaccine adjuvanted with (R)-DOTAP inhibits tumor growth in an advanced melanoma model
Abstract
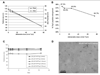
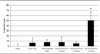
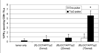
Previously we have shown cationic lipid (R)-DOTAP as the immunologically active enantiomer of the DOTAP racemic mixture, initiating complete tumor regression in an exogenous antigen model (murine cervical cancer model). Here, we investigate the use of (R)-DOTAP as an efficacious adjuvant delivering an endogenous antigen in an aggressive murine solid tumor melanoma model. (R)-DOTAP/Trp2 peptide complexes showed decreasing size and charge with increasing peptide concentration, taking a rod shape at highest concentrations. The particles were stable for 2 weeks at 4 °C. A dose of 75 nmol of Trp2 (formulated in (R)-DOTAP) was able to show statistically significant tumor growth delay compared to lower doses of 5 and 25 nmol, which were no different than untreated tumors. (R)-DOTAP/Trp2 (75 nmol) treated mice also showed increased T cell IFN-γ secretion after restimulation with Trp2, as well as CTL activity in vivo. This vaccination group also showed the highest population of functionally active tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, indicated by IFN-γ secretion after restimulation with Trp2. Thus, (R)-DOTAP has shown the ability to break tolerance as an adjuvant. Its activity to enhance immunogenicity of other tumor associated antigens should be studied further.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Enantiospecific adjuvant activity of cationic lipid DOTAP in cancer vaccine.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 May;60(5):629-38. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-0970-1. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21267720 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of salt on the physicochemical properties and immunogenicity of protein based vaccine formulated in cationic liposome.Int J Pharm. 2009 Feb 23;368(1-2):56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.09.053. Epub 2008 Oct 15. Int J Pharm. 2009. PMID: 18992312 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional nanoparticles co-delivering Trp2 peptide and CpG adjuvant induce potent cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response against melanoma and its lung metastasis.J Control Release. 2013 Nov 28;172(1):259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Sep 1. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 24004885
-
Poly (I:C)-DOTAP cationic nanoliposome containing multi-epitope HER2-derived peptide promotes vaccine-elicited anti-tumor immunity in a murine model.Immunol Lett. 2016 Aug;176:57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2016.05.016. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Immunol Lett. 2016. PMID: 27260485
-
Antigen Priming with Enantiospecific Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles Induces Potent Antitumor CTL Responses through Novel Induction of a Type I IFN Response.J Immunol. 2019 Jun 15;202(12):3524-3536. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801634. Epub 2019 May 3. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31053626 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recombinant Protein Vaccines Formulated with Enantio-Specific Cationic Lipid R-DOTAP Induce Protective Cellular and Antibody-Mediated Immune Responses in Mice.Viruses. 2023 Feb 4;15(2):432. doi: 10.3390/v15020432. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851646 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured SL9-CpG Lipovaccines Elicit Immune Response for the Treatment of Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 5;20(9):2207. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092207. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31060324 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology Approaches to Improving Cancer Immunotherapy.Adv Cancer Res. 2018;139:35-56. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Adv Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29941106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innovative DNA vaccine to break immune tolerance against tumor self-antigen.Hum Gene Ther. 2013 Feb;24(2):181-8. doi: 10.1089/hum.2012.141. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Hum Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23268564 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Immune Agonist Nanoparticle Therapy Stimulates Type I Interferons to Activate Antigen-Presenting Cells and Induce Antigen-Specific Antitumor Immunity.Mol Pharm. 2021 Mar 1;18(3):1014-1025. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00984. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33541072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flaherty KT. Narrative review: BRAF opens the door for therapeutic advances in melanoma. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153:587–591. - PubMed
-
- Hersey P. Immunotherapy of melanoma. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2010;6 Suppl 1:S2–S8. - PubMed
-
- Ko JM, Fisher DE. A new era: melanoma genetics and therapeutics. J Pathol. 2011;223:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–954. - PubMed
-
- Puzanov I, Flaherty KT. Targeted molecular therapy in melanoma. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:196–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

