Arv1 lipid transporter function is conserved between pathogenic and nonpathogenic fungi
- PMID: 22142782
- PMCID: PMC3278566
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fgb.2011.11.006
Arv1 lipid transporter function is conserved between pathogenic and nonpathogenic fungi
Abstract
The lipid transporter Arv1 regulates sterol trafficking, and glycosylphosphatidylinositol and sphingolipid biosyntheses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. ScArv1 contains an Arv1 homology domain (AHD) that is conserved at the amino acid level in the pathogenic fungal species, Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Here we show S. cerevisiae cells lacking Arv1 are highly susceptible to antifungal drugs. In the presence of drug, Scarv1 cells are unable to induce ERG gene expression, have an altered pleiotrophic drug response, and are defective in multi-drug resistance efflux pump expression. All phenotypes are remediated by ectopic expression of CaARV1 or CgARV1. The AHDs of these pathogenic fungi are required for specific drug tolerance, demonstrating conservation of function. In order to understand how Arv1 regulates antifungal susceptibility, we examined sterol trafficking. CaARV1/CgARV1 expression suppressed the sterol trafficking defect of Scarv1 cells. Finally, we show that C. albicansarv1/arv1 cells are avirulent using a BALB/c disseminated mouse model. We suggest that overall cell survival in response to antifungal treatment requires the lipid transporter function of Arv1.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


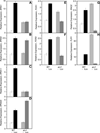
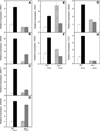






Similar articles
-
An Erg11 lanosterol 14-α-demethylase-Arv1 complex is required for Candida albicans virulence.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 17;15(7):e0235746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235746. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32678853 Free PMC article.
-
The sterol-regulating human ARV1 binds cholesterol and phospholipids through its conserved ARV1 homology domain.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108306. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108306. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39952408 Free PMC article.
-
The putative lipid transporter, Arv1, is required for activating pheromone-induced MAP kinase signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2011 Feb;187(2):455-65. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.120725. Epub 2010 Nov 23. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21098723 Free PMC article.
-
The synthesis, regulation, and functions of sterols in Candida albicans: Well-known but still lots to learn.Virulence. 2016 Aug 17;7(6):649-59. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1188236. Epub 2016 May 24. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 27221657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinate control of lipid composition and drug transport activities is required for normal multidrug resistance in fungi.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1794(5):852-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.12.012. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19150512 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mice lacking ARV1 have reduced signs of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 20;293(16):5956-5974. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000800. Epub 2018 Feb 28. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29491146 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans gains azole resistance by altering sphingolipid composition.Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 29;9(1):4495. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06944-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30374049 Free PMC article.
-
An Erg11 lanosterol 14-α-demethylase-Arv1 complex is required for Candida albicans virulence.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 17;15(7):e0235746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235746. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32678853 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of murine Arv1 results in a lean phenotype with increased energy expenditure.Nutr Diabetes. 2015 Oct 19;5(10):e181. doi: 10.1038/nutd.2015.32. Nutr Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 26479315 Free PMC article.
-
The sterol-regulating human ARV1 binds cholesterol and phospholipids through its conserved ARV1 homology domain.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108306. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108306. Epub 2025 Feb 12. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39952408 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alarco AM, et al. AP1-mediated multidrug resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires FLR1 encoding a transporter of the major facilitator superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19304–19313. - PubMed
-
- Balzi E, et al. The multidrug resistance gene PDR1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:16871–16879. - PubMed
-
- Balzi E, Goffeau A. Yeast multidrug resistance: the PDR network. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1995;27:71–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

