Differential regulation of epiboly initiation and progression by zebrafish Eomesodermin A
- PMID: 22142964
- PMCID: PMC3259739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.10.036
Differential regulation of epiboly initiation and progression by zebrafish Eomesodermin A
Abstract
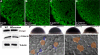
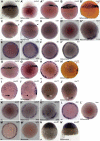
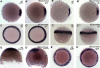
The T-box transcription factor Eomesodermin (Eomes) has been implicated in patterning and morphogenesis in frog, fish and mouse. In zebrafish, one of the two Eomes homologs, Eomesa, has been implicated in dorsal-ventral patterning, epiboly and endoderm specification in experiments employing over-expression, dominant-negative constructs and antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. Here we report for the first time the identification and characterization of an Eomesa mutant generated by TILLING. We find that Eomesa has a strictly maternal role in the initiation of epiboly, which involves doming of the yolk cell up into the overlying blastoderm. By contrast, epiboly progression is normal, demonstrating for the first time that epiboly initiation is genetically separable from progression. The yolk cell microtubules, which are required for epiboly, are defective in maternal-zygotic eomesa mutant embryos. In addition, the deep cells of the blastoderm are more tightly packed and exhibit more bleb-like protrusions than cells in control embryos. We postulate that the doming delay may be the consequence both of overly stabilized yolk cell microtubules and defects in the adhesive properties or motility of deep cells. We also show that Eomesa is required for normal expression of the endoderm markers sox32, bon and og9x; however it is not essential for endoderm formation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander J, Rothenberg M, Henry GL, Stainier DY. casanova plays an early and essential role in endoderm formation in zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 1999;215:343–357. - PubMed
-
- Alexander J, Stainier DY. A molecular pathway leading to endoderm formation in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:1147–1157. - PubMed
-
- Babb SG, Marrs JA. E-cadherin regulates cell movements and tissue formation in early zebrafish embryos. Dev. Dyn. 2004;230:263–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

