Resistance to linezolid caused by modifications at its binding site on the ribosome
- PMID: 22143525
- PMCID: PMC3264260
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05702-11
Resistance to linezolid caused by modifications at its binding site on the ribosome
Abstract
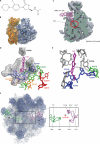
Linezolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic in clinical use for the treatment of serious infections of resistant Gram-positive bacteria. It inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome. Almost all known resistance mechanisms involve small alterations to the linezolid binding site, so this review will therefore focus on the various changes that can adversely affect drug binding and confer resistance. High-resolution structures of linezolid bound to the 50S ribosomal subunit show that it binds in a deep cleft that is surrounded by 23S rRNA nucleotides. Mutation of 23S rRNA has for some time been established as a linezolid resistance mechanism. Although ribosomal proteins L3 and L4 are located further away from the bound drug, mutations in specific regions of these proteins are increasingly being associated with linezolid resistance. However, very little evidence has been presented to confirm this. Furthermore, recent findings on the Cfr methyltransferase underscore the modification of 23S rRNA as a highly effective and transferable form of linezolid resistance. On a positive note, detailed knowledge of the linezolid binding site has facilitated the design of a new generation of oxazolidinones that show improved properties against the known resistance mechanisms.
Figures


References
-
- Barbachyn MR, Ford CW. 2003. Oxazolidinone structure-activity relationships leading to linezolid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 42:2010–2023 - PubMed
-
- Bongiorno D, et al. 2010. DNA methylase modifications and other linezolid resistance mutations in coagulase-negative staphylococci in Italy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65:2336–2340 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

