Extraction of Lepidium apetalum seed oil using supercritical carbon dioxide and anti-oxidant activity of the extracted oil
- PMID: 22143572
- PMCID: PMC6264353
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules161210029
Extraction of Lepidium apetalum seed oil using supercritical carbon dioxide and anti-oxidant activity of the extracted oil
Abstract
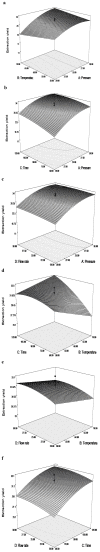
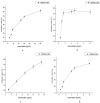
The supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) of Lepidium apetalum seed oil and its anti-oxidant activity were studied. The SFE process was optimized using response surface methodology (RSM) with a central composite design (CCD). Independent variables, namely operating pressure, temperature, time and flow rate were evaluated. The maximum extraction of Lepidium apetalum seed oil by SFE-CO₂ (about 36.3%) was obtained when SFE-CO₂ extraction was carried out under the optimal conditions of 30.0 MPa of pressure, 70 °C of temperature, 120 min of extraction time and 25.95 L/h of flow rate. GC-MS analysis showed the presence of four fatty acids in Lepidium apetalum seed oil, with a high content (91.0%) of unsaturated fatty acid. The anti-oxidant activity of the oil was assessed by the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical-scavenging assay and 2,2'-azino- bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS) test. Lepidium apetalum seed oil possessed a notable concentration-dependent antioxidant activity, with IC₅₀ values of 1.00 and 3.75 mg/mL, respectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia. 1st. TCM Science and Technology Publishing House; Beijing, China: 2010. p. 313.
-
- Kai S., Li X. Progress in Studies on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Effect of Lepidium apetalum and Semen Descurainiae. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2002;33:3–5.
-
- Zhao H.Y., Fan M.X., Shi J.L., Wang A.Q., Li J.L. Isolation and Structure Identification of Chemical Constituents from Seeds of Lepidium apetalum. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2010;1:14–18.
-
- Wu X.L., Yang Y.Z., Huang D.L. The Effect of Left Heart Primary Function of Dogs of the Water Extraction of Lepidium apetalum. Zhong Yao Cai. 1998;21:243–245. - PubMed
-
- Ren C.F. Clinical Observation on Treatment of Heart Failure Induced By Chronic Pneumocardial Disease By Lepidium apetalum. Proc. Clin. Med. 2005;14:933.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

