Clinical course of patients with episodic cluster headache treated with corticosteroids inproximity to the sphenopalatine ganglion: a preliminary study of 23 patients
- PMID: 22143727
- PMCID: PMC3476098
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.17578
Clinical course of patients with episodic cluster headache treated with corticosteroids inproximity to the sphenopalatine ganglion: a preliminary study of 23 patients
Abstract
Objective: A study is made of the clinical course of patients with episodic cluster headache following the injection of corticosteroids in the proximity of the sphenopalatine ganglion of the affected side.
Study design: A retrospective observation study was made corresponding to the period between 2006 and 2010. Patients with episodic cluster headache received corticosteroid infiltrations in the vicinity of the sphenopalatine ganglion. Data were collected to assess the clinical course, quantifying pain intensity and quality of life. A total of 23 patients (11 women and 12 men) with a mean age of 50.4 years (range 25-65) were included. Forty percent of the patients had undergone dental extractions in the quadrant affected by the pain, before the development of episodic cluster headache, and 37.8% underwent extractions in the same quadrant after appearance of the headache.
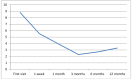
Results: Most of the patients suffered 1-3 attacks a day, with a duration of pain of between 31-90 minutes. The mean pain intensity score during the attacks at the time of the first visit was 8.8 (range 6-10), versus 5.4 (range 3-9) one week after the first corticosteroid injection. On the first visit, 86.9% of the patients reported unbearable pain, versus 21.7% after one week, and a single patient after one month.
Conclusions: The evolution of episodic cluster headache is unpredictable and variable, though corticosteroid administration clearly reduces the attacks and their duration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Acupuncture at sphenopalatine ganglion combined with conventional acupuncture for episodic cluster headache: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022 Jun 12;42(6):603-7. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20211111-k0007. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35712941 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Role of sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation in cluster headache.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014 Jul;18(7):433. doi: 10.1007/s11916-014-0433-4. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2014. PMID: 24880803 Review.
-
Chronic Bilateral Sphenopalatine Ganglion Stimulation for Intractable Bilateral Chronic Cluster Headache: A Case Report.Pain Physician. 2016 May;19(4):E637-42. Pain Physician. 2016. PMID: 27228531
-
Open-Label, Multi-Dose, Pilot Safety Study of Injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA Toward the Otic Ganglion for the Treatment of Intractable Chronic Cluster Headache.Headache. 2020 Sep;60(8):1632-1643. doi: 10.1111/head.13889. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Headache. 2020. PMID: 32583902 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of sphenopalatine ganglion neuroablation in the management of cluster headache.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2010 Apr;14(2):160-3. doi: 10.1007/s11916-010-0100-3. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2010. PMID: 20425206 Review.
Cited by
-
Cluster headache: crosspoint between otologists and neurologists-treatment of the sphenopalatine ganglion and systematic review.Neurol Sci. 2019 May;40(Suppl 1):137-146. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-03796-5. Neurol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30877613
-
Multicentre, prospective, randomised, controlled, blinded-endpoint study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pterygopalatine ganglion pulsed radiofrequency treatment for cluster headache: study protocol.BMJ Open. 2019 Mar 23;9(3):e026608. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026608. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30904875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004;24:9–160. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramaniam R, Klasser GD. Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias. Part 1: cluster headache. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;104:345–58. - PubMed
-
- Felisati G, Arnone F, Lozza P, Leone M, Curone M, Bussone G. Sphenopalatine endoscopic ganglion block: a revision of a traditional technique for cluster headache. Laryngoscope. 2006;116:1447–50. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Oraee S. A novel approach to transnasal sphenopalatine ganglion injection. Pain Physician. 2006;9:131–4. - PubMed
-
- Goadsby PJ. Pathophysiology of cluster headache: a trigeminal autonomic cephalgia. Lancet Neurol. 2002;1:251–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical