Computational design of a symmetric homodimer using β-strand assembly
- PMID: 22143762
- PMCID: PMC3251150
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1115124108
Computational design of a symmetric homodimer using β-strand assembly
Abstract
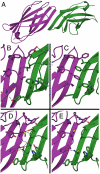
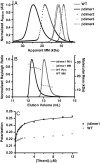
Computational design of novel protein-protein interfaces is a test of our understanding of protein interactions and has the potential to allow modification of cellular physiology. Methods for designing high-affinity interactions that adopt a predetermined binding mode have proved elusive, suggesting the need for new strategies that simplify the design process. A solvent-exposed backbone on a β-strand is thought of as "sticky" and β-strand pairing stabilizes many naturally occurring protein complexes. Here, we computationally redesign a monomeric protein to form a symmetric homodimer by pairing exposed β-strands to form an intermolecular β-sheet. A crystal structure of the designed complex closely matches the computational model (rmsd = 1.0 Å). This work demonstrates that β-strand pairing can be used to computationally design new interactions with high accuracy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

