Antigen-specific induced Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are generated following CD40/CD154 blockade
- PMID: 22143783
- PMCID: PMC3251074
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1105500108
Antigen-specific induced Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are generated following CD40/CD154 blockade
Abstract
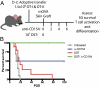
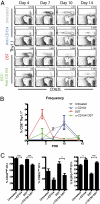
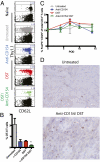
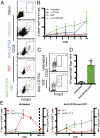
Blockade of the CD40/CD154 pathway potently attenuates T-cell responses in models of autoimmunity, inflammation, and transplantation. Indeed, CD40 pathway blockade remains one of the most powerful methods of prolonging graft survival in models of transplantation. But despite this effectiveness, the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the protective effects of CD40 pathway blockade are incompletely understood. Furthermore, the relative contributions of deletion, anergy, and regulation have not been measured in a model in which donor-reactive CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell responses can be assessed simultaneously. To investigate the impact of CD40/CD154 pathway blockade on graft-specific T-cell responses, a transgenic mouse model was used in which recipients containing ovalbumin-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) TCR transgenic T cells were grafted with skin expressing ovalbumin in the presence or absence of anti-CD154 and donor-specific transfusion. The results indicated that CD154 blockade altered the kinetics of donor-reactive CD8(+) T-cell expansion, delaying differentiation into IFN-γ(+) TNF(+) multifunctional cytokine producers. The eventual differentiation of cytokine-producing effectors in tolerant animals coincided with the emergence of an antigen-specific CD4(+) CD25(hi) Foxp3(+) T-cell population, which did not arise from endogenous natural T(reg) but rather were peripherally generated from naïve Foxp3(-) precursors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An anti-CD154 domain antibody prolongs graft survival and induces Foxp3(+) iTreg in the absence and presence of CTLA-4 Ig.Am J Transplant. 2013 Nov;13(11):3021-30. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12417. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 24007441 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CD8+ T cell-derived CD40 signals is necessary but not sufficient for Foxp3+ induced regulatory T cell generation in vivo.J Immunol. 2013 Aug 15;191(4):1957-64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300267. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23858029 Free PMC article.
-
Differential induction of donor-reactive Foxp3+ regulatory T cell via blockade of CD154 vs CD40.Am J Transplant. 2024 Aug;24(8):1369-1381. doi: 10.1016/j.ajt.2024.03.033. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Am J Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38552961 Free PMC article.
-
Dependency of direct pathway CD4+ T cells on CD40-CD154 costimulation is determined by nature and microenvironment of primary contact with alloantigen.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 15;172(4):2163-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.4.2163. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14764682
-
The effect of age on the cognate function of CD4+ T cells.Immunol Rev. 2005 Jun;205:220-8. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2005.00255.x. Immunol Rev. 2005. PMID: 15882356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of infection on transplantation tolerance.Immunol Rev. 2019 Nov;292(1):243-263. doi: 10.1111/imr.12803. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31538351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral alloantigen exposure promotes donor-specific tolerance in a mouse model of minor-mismatched skin transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2022 Oct;22(10):2348-2359. doi: 10.1111/ajt.17107. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35633180 Free PMC article.
-
In or out of control: Modulating regulatory T cell homeostasis and function with immune checkpoint pathways.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;13:1033705. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1033705. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591244 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle delivery of CD40 siRNA suppresses alloimmune responses by inhibiting activation and differentiation of DCs and macrophages.Sci Adv. 2022 Dec 21;8(51):eabq3699. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq3699. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36542700 Free PMC article.
-
An anti-CD154 domain antibody prolongs graft survival and induces Foxp3(+) iTreg in the absence and presence of CTLA-4 Ig.Am J Transplant. 2013 Nov;13(11):3021-30. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12417. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Am J Transplant. 2013. PMID: 24007441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirk AD, et al. Treatment with humanized monoclonal antibody against CD154 prevents acute renal allograft rejection in nonhuman primates. Nat Med. 1999;5:686–693. - PubMed
-
- Larsen CP, et al. CD40-gp39 interactions play a critical role during allograft rejection: Suppression of allograft rejection by blockade of the CD40-gp39 pathway. Transplantation. 1996;61:4–9. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Andrews D, Colvin RB, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB. Thromboembolic complications after treatment with monoclonal antibody against CD40 ligand. Nat Med. 2000;6:114. - PubMed
-
- Henn V, et al. CD40 ligand on activated platelets triggers an inflammatory reaction of endothelial cells. Nature. 1998;391:591–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

