Sterile inflammation of endothelial cell-derived apoptotic bodies is mediated by interleukin-1α
- PMID: 22143786
- PMCID: PMC3251090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1116848108
Sterile inflammation of endothelial cell-derived apoptotic bodies is mediated by interleukin-1α
Abstract
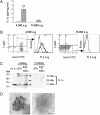
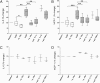
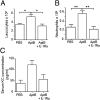
Sterile inflammation resulting from cell death is due to the release of cell contents normally inactive and sequestered within the cell; fragments of cell membranes from dying cells also contribute to sterile inflammation. Endothelial cells undergoing stress-induced apoptosis release membrane microparticles, which become vehicles for proinflammatory signals. Here, we show that stress-activated endothelial cells release two distinct populations of particles: One population consists of membrane microparticles (<1 μm, annexin V positive without DNA and no histones) and another larger (1-3 μm) apoptotic body-like particles containing nuclear fragments and histones, representing apoptotic bodies. Contrary to present concepts, endothelial microparticles do not contain IL-1α and do not induce neutrophilic chemokines in vitro. In contrast, the large apoptotic bodies contain the full-length IL-1α precursor and the processed mature form. In vitro, these apoptotic bodies induce monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and IL-8 chemokine secretion in an IL-1α-dependent but IL-1β-independent fashion. Injection of these apoptotic bodies into the peritoneal cavity of mice induces elevated serum neutrophil-inducing chemokines, which was prevented by cotreatment with the IL-1 receptor antagonist. Consistently, injection of these large apoptotic bodies into the peritoneal cavity induced a neutrophilic infiltration that was prevented by IL-1 blockade. Although apoptosis is ordinarily considered noninflammatory, these data demonstrate that nonphagocytosed endothelial apoptotic bodies are inflammatory, providing a vehicle for IL-1α and, therefore, constitute a unique mechanism for sterile inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Kroemer G. Decoding cell death signals in inflammation and immunity. Cell. 2010;140:798–804. - PubMed
-
- Rider P, et al. IL-1alpha and IL-1beta recruit different myeloid cells and promote different stages of sterile inflammation. J Immunol. 2011;187:4835–4843. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:519–550. - PubMed
-
- Kurt-Jones EA, Fiers W, Pober JS. Membrane interleukin 1 induction on human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1987;139:2317–2324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

