Characteristics of Borrelia hermsii infection in human hematopoietic stem cell-engrafted mice mirror those of human relapsing fever
- PMID: 22143787
- PMCID: PMC3251092
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1108776109
Characteristics of Borrelia hermsii infection in human hematopoietic stem cell-engrafted mice mirror those of human relapsing fever
Abstract
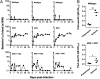
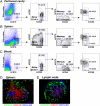
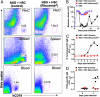
Rodents are natural reservoirs for a variety of species of Borrelia that cause relapsing fever (RF) in humans. The murine model of this disease recapitulates many of the clinical manifestations of the human disease and has revealed that T cell-independent antibody responses are required to resolve the bacteremic episodes. However, it is not clear whether such protective humoral responses are mounted in humans. We examined Borrelia hermsii infection in human hematopoietic stem cell-engrafted nonobese diabetic/SCID/IL-2Rγ(null) mice: "human immune system mice" (HISmice). Infection of these mice, which are severely deficient in lymphoid and myeloid compartments, with B. hermsii resulted in persistent bacteremia. In contrast, this infection in HISmice resulted in recurrent episodes of bacteremia, the hallmark of RF. The resolution of the primary episode of bacteremia was concurrent with the generation of B. hermsii-specific human IgM. Remarkably, HISmice generated antibody responses to the B. hermsii outer-membrane protein Factor H binding protein A. Sera from humans infected by B. hermsii have a similar reactivity, and studies in mice have shown that this response is generated by the B1b cell subset. HISmice contain several B-cell subsets, including those with the phenotype CD20(+)CD27(+)CD43(+)CD70(-), a proposed human equivalent of mouse B1 cells. Reduction of B cells by administration of anti-human CD20 antibody resulted in diminished anti-B. hermsii responses and persistent bacteremia in HISmice. These data indicate that analysis of B. hermsii infection in HISmice will serve as a model in which to study the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in controlling human RF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The resolution of relapsing fever borreliosis requires IgM and is concurrent with expansion of B1b lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 1;170(7):3819-27. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.7.3819. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12646649
-
Toll-like receptor 2 deficiency results in impaired antibody responses and septic shock during Borrelia hermsii infection.Infect Immun. 2010 Nov;78(11):4579-88. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00438-10. Epub 2010 Aug 9. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20696824 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient B cell responses to Borrelia hermsii infection depend on BAFF and BAFFR but not TACI.Infect Immun. 2014 Jan;82(1):453-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01147-13. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24218480 Free PMC article.
-
B1b lymphocyte-derived antibodies control Borrelia hermsii independent of Fcα/μ receptor and in the absence of host cell contact.Immunol Res. 2011 Dec;51(2-3):249-56. doi: 10.1007/s12026-011-8260-8. Immunol Res. 2011. PMID: 22139824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mammalian host response to borrelia infection.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006 Nov;118(21-22):653-8. doi: 10.1007/s00508-006-0692-0. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2006. PMID: 17160603 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: persistently seronegative neuroborreliosis in an immunocompromised patient.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Aug 2;18(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3273-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30071836 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue virus infection induces broadly cross-reactive human IgM antibodies that recognize intact virions in humanized BLT-NSG mice.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Jan;240(1):67-78. doi: 10.1177/1535370214546273. Epub 2014 Aug 14. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25125497 Free PMC article.
-
Humanized Mouse Model Mimicking Pathology of Human Tuberculosis for in vivo Evaluation of Drug Regimens.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 31;10:89. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00089. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30766535 Free PMC article.
-
Borrelia spielmanii-Associated Neuroborreliosis in Patient Receiving Rituximab, Belgium.Emerg Infect Dis. 2025 Feb;31(2):341-344. doi: 10.3201/eid3102.240777. Emerg Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39983686 Free PMC article.
-
Human B-1 and B-2 B Cells Develop from Lin-CD34+CD38lo Stem Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Nov 15;197(10):3950-3958. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600630. Epub 2016 Oct 7. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27815443 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Southern PM, Jr, Sanford JP. Relapsing fever: A clinical and microbiological review. Medicine. 1969;48:129–149.
-
- Cadavid D, Barbour AG. Neuroborreliosis during relapsing fever: Review of the clinical manifestations, pathology, and treatment of infections in humans and experimental animals. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:151–164. - PubMed
-
- Burgdorfer W. The epidemiology of the relapsing fevers. In: Johnson RC, editor. The Biology of Parasitic Spirochetes. New York: Academic; 1976. pp. 191–200.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

