An overview of targeted alpha therapy
- PMID: 22143940
- PMCID: PMC7450491
- DOI: 10.1007/s13277-011-0286-y
An overview of targeted alpha therapy
Abstract
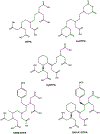
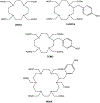
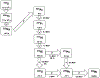
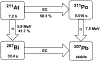
The effectiveness of targeted α-therapy (TAT) can be explained by the properties of α-particles. Alpha particles are helium nuclei and are ~8,000 times larger than β(-)-particles (electrons). When emitted from radionuclides that decay via an α-decay pathway, they release enormous amounts of energy over a very short distance. Typically, the range of α-particles in tissue is 50-100 μm and they have high linear energy transfer (LET) with a mean energy deposition of 100 keV/μm, providing a more specific tumor cell killing ability without damage to the surrounding normal tissues than β(-)-emitters. Due to these properties, the majority of pre-clinical and clinical trials have demonstrated that α-emitters such as (225)Ac, (211)At, (212)Bi, (213)Bi, (212)Pb, (223)Ra, and (227)Th are ideal for the treatment of smaller tumor burdens, micrometastatic disease, and disseminated disease. Even though these α-emitters have favorable properties, the development of TAT has been limited by high costs, unresolved chemistry, and limited availability of the radionuclides. To overcome these limitations, more potent isotopes, additional sources, and more efficient isotope production methods should be addressed. Furthermore, better chelation and labeling methods with the improvements of isotope delivery, targeting vehicles, molecular targets, and identification of appropriate clinical applications are still required.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Sgouros G, Ballangrud AM, Jurcic JG, McDevitt MR, Humm JL, Erdi YE, Mehta BM, Finn RD, Larson SM, Scheinberg DA. Pharmacokinetics and dosimetry of an α-particle emitter antibody: 213Bi-HuM195 (anti-CD33) in patients with leukemia. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:1935–46. - PubMed
-
- Zalutsky MR, Bigner DD. Radioimmunotherpy with α-particle emitting radioimmunoconjugates. Acta Oncol. 1996;35:373–9. - PubMed
-
- Zalutsky MR, Schuster JM, Garg PK, Archer GE, DeWhirst MW, Binger DD. Two approaches for enhancing radioimmunotherapy: alpha emitters and hyperthermia. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1996;141:101–22. - PubMed
-
- Nikula TK, McDevitt MR, Finn RD, Wu CC, Kozak RW, Garmestani K, Brechbiel MW, Curcio ML, Pippin CG, Tiffany-Jones L, Geerlings MW, Apostolidis C, Molinet R, Gansow OA, Sheinberg DA. Alpha-emitting bismuth cyclohexylbenzyl DTPA constructs of recombinant humanized anti-CD33 antibodies: pharmacokinetics, bioactivity, toxicity and chemistry. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:166–76. - PubMed
-
- Raju MR, Eisen Y, Carpenter S, Inkret WC. Radiobiology of alpha-particles. 3. Cell inactivation by alpha-particle traversals of the cell-nucleus. Radiat Res. 1991;128:204–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources