KLF9 is a novel transcriptional regulator of bortezomib- and LBH589-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells
- PMID: 22144178
- PMCID: PMC3286209
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-346676
KLF9 is a novel transcriptional regulator of bortezomib- and LBH589-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells
Abstract
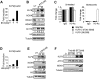
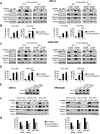
Bortezomib, a therapeutic agent for multiple myeloma (MM) and mantle cell lymphoma, suppresses proteosomal degradation leading to substantial changes in cellular transcriptional programs and ultimately resulting in apoptosis. Transcriptional regulators required for bortezomib-induced apoptosis in MM cells are largely unknown. Using gene expression profiling, we identified 36 transcription factors that displayed altered expression in MM cells treated with bortezomib. Analysis of a publically available database identified Kruppel-like family factor 9 (KLF9) as the only transcription factor with significantly higher basal expression in MM cells from patients who responded to bortezomib compared with nonresponders. We demonstrated that KLF9 in cultured MM cells was up-regulated by bortezomib; however, it was not through the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Instead, KLF9 levels correlated with bortezomib-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDAC) and were increased by the HDAC inhibitor LBH589 (panobinostat). Furthermore, bortezomib induced binding of endogenous KLF9 to the promoter of the proapoptotic gene NOXA. Importantly, KLF9 knockdown impaired NOXA up-regulation and apoptosis caused by bortezomib, LBH589, or a combination of theses drugs, whereas KLF9 overexpression induced apoptosis that was partially NOXA-dependent. Our data identify KLF9 as a novel and potentially clinically relevant transcriptional regulator of drug-induced apoptosis in MM cells.
Figures
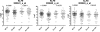
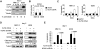
Similar articles
-
Role of CAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein in panobinostat-mediated potentiation of bortezomib-induced lethal endoplasmic reticulum stress in mantle cell lymphoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Oct 1;16(19):4742-54. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0529. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20647473 Free PMC article.
-
Noxa up-regulation and Mcl-1 cleavage are associated to apoptosis induction by bortezomib in multiple myeloma.Cancer Res. 2007 Jun 1;67(11):5418-24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4322. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17545623
-
Synergistic induction of oxidative injury and apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and histone deacetylase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Jun 1;10(11):3839-52. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0561. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15173093
-
[Determinants of sensitivity to proteasome inhibitors and strategies to overcome acquired resistance to bortezomib in multiple myeloma].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2014 Mar;55(3):304-10. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2014. PMID: 24681933 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Krüppel-like Factor-9 and Krüppel-like Factor-13: Highly Related, Multi-Functional, Transcriptional Repressors and Activators of Oncogenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;15(23):5667. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235667. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chromothripsis in Treatment Resistance in Multiple Myeloma.Genomics Inform. 2017 Sep;15(3):87-97. doi: 10.5808/GI.2017.15.3.87. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Genomics Inform. 2017. PMID: 29020724 Free PMC article.
-
Racial disparities, cancer and response to oxidative stress.Adv Cancer Res. 2019;144:343-383. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Adv Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31349903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postpartum scarcity-adversity inflicts sex-specific cerebellar adaptations and reward behaviors in adolescence.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2023 Oct;231:173620. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2023.173620. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2023. PMID: 37625522 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 amplifies oxidative stress via induction of Klf9.Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 20;53(6):916-928. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.033. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24613345 Free PMC article.
-
Homopiperazine derivatives as a novel class of proteasome inhibitors with a unique mode of proteasome binding.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 11;8(4):e60649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060649. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23593271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson KC. Bortezomib therapy for myeloma. Curr Hematol Rep. 2004;3(1):65. - PubMed
-
- Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Raab MS, Podar K, Breitkreutz I, et al. Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 2009;374(9686):324–339. - PubMed
-
- Venner CP, Connors JM, Sutherland HJ, et al. Novel agents improve survival of transplant patients with multiple myeloma including those with high-risk disease defined by early relapse (< 12 months). Leuk Lymphoma. 2011;52(1):34–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

