Mitochondrial dysfunction in ataxia-telangiectasia
- PMID: 22144182
- PMCID: PMC3286212
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-373639
Mitochondrial dysfunction in ataxia-telangiectasia
Abstract
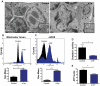
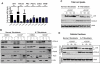
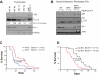
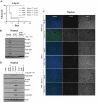
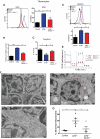
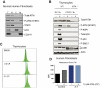
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) plays a central role in DNA damage responses, and its loss leads to development of T-cell malignancies. Here, we show that ATM loss also leads to intrinsic mitochondrial abnormalities in thymocytes, including elevated reactive oxygen species, increased aberrant mitochondria, high cellular respiratory capacity, and decreased mitophagy. A fraction of ATM protein is localized in mitochondria, and it is rapidly activated by mitochondrial dysfunction. Unexpectedly, allelic loss of the autophagy regulator Beclin-1 significantly delayed tumor development in ATM-null mice. This effect was not associated with rescue of DNA damage signaling but rather with a significant reversal of the mitochondrial abnormalities. These data support a model in which ATM plays direct roles in modulating mitochondrial homeostasis and suggest that mitochondrial dysfunction and associated increases in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species contribute to the cancer-prone phenotype observed in organisms lacking ATM. Thus, ataxia-telangiectasia should be considered, at least in part, as a mitochondrial disease.
Figures
References
-
- Lavin MF, Shiloh Y. Ataxia-telangiectasia–a multifaceted genetic disorder associated with defective signal transduction. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:459–464. - PubMed
-
- Herzog K-H, Chong MJ, Kapsetaki M, Morgan JI, McKinnon PJ. Requirement for Atm in ionizing radiation-induced cell death in the developing central nervous system. Science. 1998;280:1089–1091. - PubMed
-
- Barlow C, Hirotsune S, Paylor R, et al. Atm-deficient mice: a paradigm of ataxia telangiectasia. Cell. 1996;86:159–171. - PubMed
-
- Lavin MF. Ataxia-telangiectasia: from a rare disorder to a paradigm for cell signalling and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(10):759–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

