Heterogeneity of astrocytic form and function
- PMID: 22144298
- PMCID: PMC3506190
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-61779-452-0_3
Heterogeneity of astrocytic form and function
Abstract
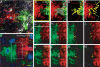
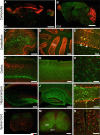
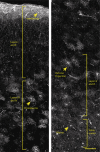
Astrocytes participate in all essential CNS functions, including blood flow regulation, energy metabolism, ion and water homeostasis, immune defence, neurotransmission, and adult neurogenesis. It is thus not surprising that astrocytic morphology and function differ between regions, and that different subclasses of astrocytes exist within the same brain region. Recent lines of work also show that the complexity of protoplasmic astrocytes increases during evolution. Human astrocytes are structurally more complex, larger, and propagate calcium signals significantly faster than rodent astrocytes. In this chapter, we review the diversity of astrocytic form and function, while considering the markedly expanded roles of astrocytes with phylogenetic evolution. We also define major challenges for the future, which include determining how astrocytic functions are locally specified, defining the molecular controls upon astrocytic fate and physiology and establishing how evolutionary changes in astrocytes contribute to higher cognitive functions.
Figures


References
-
- Virchow RLK. Die cellularpathologie in ihrer begründung auf physiologische und pathologische gewebelehre. A. Hirschwald; Berlin: 1858. - PubMed
-
- Golgi C. Contribuzione alla fina Anatomia degli organi centrali del sistema nervosos. Rivista clinica di Bologna; Bologna: 1871.
-
- Lenhossek M. Der feinere Bau des Nervensystems im Lichte neuester Forschung. Fischer's Medicinische Buchhandlung; Berlin: 1893.
-
- Kölliker A. Handbuch der gewebelehre des menschen. 1889. p. 6. umgearb. aufl. ed., n.p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

