Selective mGluR1 antagonist EMQMCM inhibits the kainate-induced excitotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures and in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 22144346
- PMCID: PMC3296950
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-011-9293-4
Selective mGluR1 antagonist EMQMCM inhibits the kainate-induced excitotoxicity in primary neuronal cultures and in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
Abundant evidence suggests that indirect inhibitory modulation of glutamatergic transmission, via metabotropic glutamatergic receptors (mGluR), may induce neuroprotection. The present study was designed to determine whether the selective antagonist of mGluR1 (3-ethyl-2-methyl-quinolin-6-yl)-(4-methoxy-cyclohexyl)-methanone methanesulfonate (EMQMCM), showed neuroprotection against the kainate (KA)-induced excitotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. In in vitro studies on mouse primary cortical and hippocampal neuronal cultures, incubation with KA (150 μM) induced strong degeneration [measured as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) efflux] and apoptosis (measured as caspase-3 activity). EMQMCM (0.1-100 μM) added 30 min to 6 h after KA, significantly attenuated the KA-induced LDH release and prevented the increase in caspase-3 activity in the cultures. Those effects were dose- and time-dependent. In in vivo studies KA (2.5 nmol/1 μl) was unilaterally injected into the rat dorsal CA1 hippocampal region. Degeneration was calculated by counting surviving neurons in the CA pyramidal layer using stereological methods. It was found that EMQMCM (5-10 nmol/1 μl) injected into the dorsal hippocampus 30 min, 1 h, or 3 h (the higher dose only) after KA significantly prevented the KA-induced neuronal degeneration. In vivo microdialysis studies in rat hippocampus showed that EMQMCM (100 μM) significantly increased γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and decreased glutamate release. When perfused simultaneously with KA, EMQMCM substantially increased GABA release and prevented the KA-induced glutamate release. The obtained results indicate that the mGluR1 antagonist, EMQMCM, may exert neuroprotection against excitotoxicity after delayed treatment (30 min to 6 h). The role of enhanced GABAergic transmission in the neuroprotection is postulated.
© The Author(s) 2011. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com
Figures




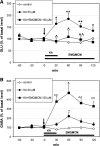
Similar articles
-
Group III mGlu receptor agonist, ACPT-I, exerts potential neuroprotective effects in vitro and in vivo.Neurotox Res. 2014 Jul;26(1):99-113. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9455-7. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Neurotox Res. 2014. PMID: 24402869 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective potential of mGluR5 antagonist MTEP: effects on kainate-induced excitotoxicity in the rat hippocampus.Pharmacol Rep. 2010 Nov-Dec;62(6):1051-61. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(10)70367-4. Pharmacol Rep. 2010. PMID: 21273662
-
Neuroprotective effects of MTEP, a selective mGluR5 antagonists and neuropeptide Y on the kainate-induced toxicity in primary neuronal cultures.Pharmacol Rep. 2006 Nov-Dec;58(6):846-58. Pharmacol Rep. 2006. PMID: 17220542
-
Ropivacaine Protects against Memory Impairment and Hippocampal Damage in a Rat Neurodegeneration Model.Pharmacology. 2018;102(5-6):307-315. doi: 10.1159/000493145. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Pharmacology. 2018. PMID: 30257255
-
Neuroprotective activity of selective mGlu1 and mGlu5 antagonists in vitro and in vivo.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jan 5;554(1):18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.09.061. Epub 2006 Oct 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17109843
Cited by
-
Trkb-IP3 Pathway Mediating Neuroprotection in Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Cell Culture Following Induction of Kainic Acid.Malays J Med Sci. 2018 Nov;25(6):28-45. doi: 10.21315/mjms2018.25.6.4. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Malays J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30914877 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin Prevents Glutamate Uptake Reduction Induced by Quinolinic Acid Via MAPKs Signaling.Neurochem Res. 2016 Aug;41(8):2017-28. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1913-1. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27084771
-
Group III mGlu receptor agonist, ACPT-I, exerts potential neuroprotective effects in vitro and in vivo.Neurotox Res. 2014 Jul;26(1):99-113. doi: 10.1007/s12640-013-9455-7. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Neurotox Res. 2014. PMID: 24402869 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins protect against kainic acid-induced excitotoxicity and apoptosis via ROS-activated AMPK pathway in hippocampal neurons.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014 Apr;20(4):327-38. doi: 10.1111/cns.12218. Epub 2014 Jan 7. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014. PMID: 24393263 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neural stem cells are more susceptible to the neurotoxin BMAA than primary neurons: effects on apoptosis, cellular differentiation, neurite outgrowth, and DNA methylation.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Oct 24;11(10):910. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03093-6. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33099583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

