Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence regulation by two bacterial adrenergic kinases, QseC and QseE
- PMID: 22144490
- PMCID: PMC3264324
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05921-11
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli virulence regulation by two bacterial adrenergic kinases, QseC and QseE
Abstract
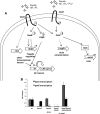
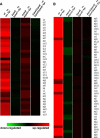
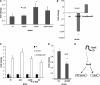
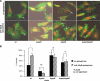
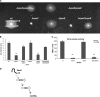
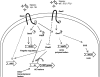
The human pathogen enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 has two histidine sensor kinases, QseC and QseE, which respond to the mammalian adrenergic hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine by increasing their autophosphorylation. Although QseC and QseE are present in nonpathogenic strains of E. coli, EHEC exploits these kinases for virulence regulation. To further investigate the full extent of epinephrine and its sensors' impact on EHEC virulence, we performed transcriptomic and phenotypic analyses of single and double deletions of qseC and qseE genes in the absence or presence of epinephrine. We showed that in EHEC, epinephrine sensing seems to occur primarily through QseC and QseE. We also observed that QseC and QseE regulate expression of the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) genes positively and negatively, respectively. LEE activation, which is required for the formation of the characteristic attaching and effacing (A/E) lesions by EHEC on epithelial cells, is epinephrine dependent. Regulation of the LEE and the non-LEE-contained virulence factor gene nleA by QseE is indirect, through transcription inhibition of the RcsB response regulator. Finally, we show that coincubation of HeLa cells with epinephrine increases EHEC infectivity in a QseC- and QseE-dependent manner. These results genetically and phenotypically map the contributions of the two adrenergic sensors QseC and QseE to EHEC pathogenesis.
Figures

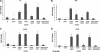
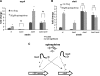
Similar articles
-
Bacterial Adrenergic Sensors Regulate Virulence of Enteric Pathogens in the Gut.mBio. 2016 Jun 7;7(3):e00826-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00826-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27273829 Free PMC article.
-
The QseC adrenergic signaling cascade in Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC).PLoS Pathog. 2009 Aug;5(8):e1000553. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000553. Epub 2009 Aug 21. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19696934 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Mechanistic Analyses of the Periplasmic Domain of the Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli QseC Histidine Sensor Kinase.J Bacteriol. 2017 Mar 28;199(8):e00861-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00861-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28138098 Free PMC article.
-
QseBC, a two-component bacterial adrenergic receptor and global regulator of virulence in Enterobacteriaceae and Pasteurellaceae.Mol Oral Microbiol. 2016 Oct;31(5):379-97. doi: 10.1111/omi.12138. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26426681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Epinephrine/Norepinephrine/Autoinducer-3 Interkingdom Signaling System in Escherichia coli O157:H7.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;874:247-61. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20215-0_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26589223 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay between the QseC and QseE bacterial adrenergic sensor kinases in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2012 Dec;80(12):4344-53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00803-12. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 23027532 Free PMC article.
-
Response of Vibrio cholerae to the Catecholamine Hormones Epinephrine and Norepinephrine.J Bacteriol. 2015 Dec;197(24):3769-78. doi: 10.1128/JB.00345-15. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 26416829 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial signaling as an antimicrobial target.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020 Oct;57:78-86. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32916624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sympathetic-Immune Milieu in Metabolic Health and Diseases: Insights from Pancreas, Liver, Intestine, and Adipose Tissues.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Feb;11(8):e2306128. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306128. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38039489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of the Microbiota and Virulence Gene Expression in E. coli O157:H7 in Pig Ligated Intestine with and without AE Lesions.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 19;10(6):e0130272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130272. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26090813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey MT, Karaszewski JW, Lubach GR, Coe CL, Lyte M. 1999. In vivo adaptation of attenuated Salmonella typhimurium results in increased growth upon exposure to norepinephrine. Physiol. Behav. 67:359–364 - PubMed
-
- Bearson BL, Bearson SM. 2008. The role of the QseC quorum-sensing sensor kinase in colonization and norepinephrine-enhanced motility of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 44:271–278 - PubMed
-
- Bearson BL, Bearson SM, Lee IS, Brunelle BW. 2010. The Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium QseB response regulator negatively regulates bacterial motility and swine colonization in the absence of the QseC sensor kinase. Microb. Pathog. 48:214–219 - PubMed
-
- Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP. 2003. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19:185–193 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

