Roles of interleukin-17 in an experimental Legionella pneumophila pneumonia model
- PMID: 22144493
- PMCID: PMC3294673
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.05544-11
Roles of interleukin-17 in an experimental Legionella pneumophila pneumonia model
Abstract
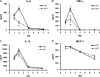
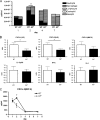
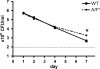
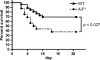
Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is a key factor in T helper type 17 (Th17) lineage host responses and plays critical roles in immunological control of a variety of infectious diseases. Although Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular bacterium found widely in the environment, often causes a serious and life-threatening pneumonia in humans, the contribution of IL-17 to immune function during Legionella pneumonia is unknown. In the present study, we used an experimental Legionella pneumonia infection to clarify the role of IL-17 in the resulting immune response. We observed robust production of pulmonary IL-17A and IL-17F (IL-17A/F), peaking on day 1 and declining thereafter. Upregulated production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-6, and IL-1β, but not monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1), was observed in Legionella-infected bone marrow-derived macrophages from BALB/c mice that had been stimulated with IL-17A or IL-17F. A significant decrease in the production of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α was observed in IL-17A/F-deficient mice (BALB/c background) infected with L. pneumophila. Moreover, we found impaired neutrophil migration and lower numbers of chemokines (KC, LIX, and MIP-2) in IL-17A/F-deficient mice. IL-17A/F-deficient mice also eliminated L. pneumophila more slowly and were less likely to survive a lethal challenge. These results demonstrate that IL-17A/F plays a critical role in L. pneumophila pneumonia, probably through induction of proinflammatory cytokines and accumulation of neutrophils at the infection site.
Figures
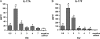
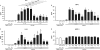
Similar articles
-
Overlapping Roles for Interleukin-36 Cytokines in Protective Host Defense against Murine Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia.Infect Immun. 2018 Dec 19;87(1):e00583-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00583-18. Print 2019 Jan. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30323031 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Toll-like receptor 2 in recognition of Legionella pneumophila in a murine pneumonia model.J Med Microbiol. 2007 Mar;56(Pt 3):305-312. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.46913-0. J Med Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17314358
-
SQSTM1/p62/A170 regulates the severity of Legionella pneumophila pneumonia by modulating inflammasome activity.Eur J Immunol. 2014 Apr;44(4):1084-92. doi: 10.1002/eji.201344091. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Eur J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24374573
-
Innate immunity against Legionella pneumophila during pulmonary infections in mice.Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Feb;40(2):131-145. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0859-9. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Arch Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28063015 Review.
-
Viewing Legionella pneumophila Pathogenesis through an Immunological Lens.J Mol Biol. 2019 Oct 4;431(21):4321-4344. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31351897 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Th17 Cells in Helicobacter pylori Infection: a Dichotomy of Help and Harm.Infect Immun. 2019 Oct 18;87(11):e00363-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00363-19. Print 2019 Nov. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31427446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of recombinant Mip-FlaA dominant epitope vaccine against Legionella pneumophila and evaluation of the immunogenicity and protective immunity.Immunol Res. 2016 Feb;64(1):272-9. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8746-x. Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 26607265
-
Overlapping Roles for Interleukin-36 Cytokines in Protective Host Defense against Murine Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia.Infect Immun. 2018 Dec 19;87(1):e00583-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00583-18. Print 2019 Jan. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30323031 Free PMC article.
-
A method for quantifying pulmonary Legionella pneumophila infection in mouse lungs by flow cytometry.BMC Res Notes. 2012 Aug 20;5:448. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-448. BMC Res Notes. 2012. PMID: 22905869 Free PMC article.
-
Localization of CD8 T cell epitope within cardiac myosin heavy chain-α334-352 that induces autoimmune myocarditis in A/J mice.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Jan 1;202:311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.09.016. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26422020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benchetrit F, et al. 2002. Interleukin-17 inhibits tumor cell growth by means of a T-cell-dependent mechanism. Blood 99:2114–2121 - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL, Miossec P. 1998. Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J. Immunol. 161:409–414 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

