MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) inhibits growth of ovarian clear cell carcinoma in a PEA-15-dependent manner in a mouse xenograft model
- PMID: 22144664
- PMCID: PMC3320047
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0400
MEK1/2 inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244) inhibits growth of ovarian clear cell carcinoma in a PEA-15-dependent manner in a mouse xenograft model
Abstract
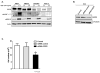
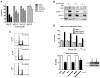
Clear cell carcinoma (CCC) of the ovary tends to show resistance to standard chemotherapy, which results in poor survival for patients with CCC. Developing a novel therapeutic strategy is imperative to improve patient prognosis. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is frequently expressed in epithelial ovarian cancer. One of the major downstream targets of the EGFR signaling cascade is extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK). PEA-15, a 15-kDa phosphoprotein, can sequester ERK in the cytoplasm. MEK1/2 plays a central role in integrating mitogenic signals into the ERK pathway. We tested the hypothesis that inhibition of the EGFR-ERK pathway suppresses tumorigenicity in CCC, and we investigated the role of PEA-15 in ERK-targeted therapy in CCC. We screened a panel of 4 CCC cell lines (RMG-I, SMOV-2, OVTOKO, and KOC-7c) and observed that the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib inhibited cell proliferation of EGFR-overexpressing CCC cell lines through partial dependence on the MEK/ERK pathway. Furthermore, erlotinib-sensitive cell lines were also sensitive to the MEK inhibitor selumetinib (AZD6244), which is under clinical development. Knockdown of PEA-15 expression resulted in reversal of selumetinib-sensitive cells to resistant cells, implying that PEA-15 contributes to selumetinib sensitivity. Both selumetinib and erlotinib significantly suppressed tumor growth (P < 0.0001) in a CCC xenograft model. However, selumetinib was better tolerated; erlotinib-treated mice exhibited significant toxic effects (marked weight loss and severe skin peeling) at high doses. Our findings indicate that the MEK-ERK pathway is a potential target for EGFR-overexpressing CCC and indicate that selumetinib and erlotinib are worth exploring as therapeutic agents for CCC.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The MEK1/2 inhibitor, selumetinib (AZD6244; ARRY-142886), enhances anti-tumour efficacy when combined with conventional chemotherapeutic agents in human tumour xenograft models.Br J Cancer. 2012 Feb 28;106(5):858-66. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.8. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Br J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22343622 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1/2 inhibition enhances the radiosensitivity of cancer cells by downregulating survival and growth signals mediated by EGFR ligands.Int J Oncol. 2013 Jun;42(6):2028-36. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1890. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23588995 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of MEK1/2 and EGFR synergistically induces caspase-3-dependent apoptosis in EGFR inhibitor-resistant lung cancer cells via BIM upregulation.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Dec;31(6):1458-65. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0030-0. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24068620
-
MEK1/2 inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic malignancies.Gynecol Oncol. 2014 Apr;133(1):128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Gynecol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24434059 Review.
-
Selumetinib in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer.Future Oncol. 2016 Nov;12(22):2545-2560. doi: 10.2217/fon-2016-0132. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27467210 Review.
Cited by
-
Xenotransplantation models to study the effects of toxicants on human fetal tissues.Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2014 Dec;101(6):410-22. doi: 10.1002/bdrb.21131. Epub 2014 Dec 4. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25477288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Src and MEK Inhibition Decreases Ovarian Cancer Growth and Targets Tumor Initiating Stem-Like Cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Oct 1;24(19):4874-4886. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3697. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29959144 Free PMC article.
-
MAPK Activation Predicts Poor Outcome and the MEK Inhibitor, Selumetinib, Reverses Antiestrogen Resistance in ER-Positive High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Feb 15;22(4):935-47. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0534. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26482043 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Small Molecule MEK Inhibitor URML-3881 Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity in Clear Cell Ovarian Cancer.Transl Oncol. 2019 Jul;12(7):917-924. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 May 10. Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31082584 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting time to ovarian carcinoma recurrence using protein markers.J Clin Invest. 2013 Sep;123(9):3740-50. doi: 10.1172/JCI68509. Epub 2013 Aug 15. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23945238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGuire V, Jesser CA, Whittemore AS. Survival among U.S. women with invasive epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2002;84:399–403. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy AW, Biscotti CV, Hart WR, Webster KD. Ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 1989;32:342–9. - PubMed
-
- Scully RE. World Health Organization classification and nomenclature of ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1975;42:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama T, Kamura T, Kigawa J, Terakawa N, Kikuchi Y, Kita T, et al. Clinical characteristics of clear cell carcinoma of the ovary: a distinct histologic type with poor prognosis and resistance to platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer. 2000;88:2584–9. - PubMed
-
- Lafky JM, Wilken JA, Baron AT, Maihle NJ. Clinical implications of the ErbB/epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor family and its ligands in ovarian cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1785:232–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

