Protective effect of lisinopril on hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
- PMID: 22144768
- PMCID: PMC3229779
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.89820
Protective effect of lisinopril on hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
Abstract
Objective: Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury plays a key role in the pathogenesis of hepatic failure in several clinical settings such as liver resection or transplantation. Lisinopril, a widely prescribed drug for various cardiovascular conditions, has been reported to have diverse pharmacological properties. The aim of this study, therefore, was to evaluate a potential protective effect of lisinopril on hepatic I/R injury in rats.
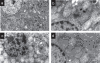
Materials and methods: In anesthetized rats, partial hepatic ischemia was applied for one hour followed by two hours reperfusion. Biochemical analysis of serum and hepatic tissue was done. Hepatic tissue was also subjected to electron microscopy.
Results: Pre-ischemic treatment with lisinopril (10 mg/kg) exerted protection against I/R-induced hepatocellular injury as evident by significant decrease in serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and total bilirubin levels, along with hepatic lipid peroxidation, expressed as malondialdehyde content, with a concurrent increase in hepatic nitric oxide content as compared to I/R group. The electron microscopic examination indicated that lisinopril can effectively protect against hepatic I/R injury.
Conclusion: Lisinopril provides a protection against hepatic I/R injury in rats. The protective effect is associated with reduction of oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation level and enhancement of nitric oxide availability.
Keywords: Ischemia/reperfusion; lisinopril; liver.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
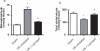
Similar articles
-
Study of the protective effect of ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning on hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury induced in rats.JGH Open. 2017 Nov 14;1(3):105-111. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12018. eCollection 2017 Nov. JGH Open. 2017. PMID: 30483545 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Wy14643 on hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Dec 7;14(45):6936-42. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6936. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 19058328 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of MESNA (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate) against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats.Surg Today. 2005;35(7):575-80. doi: 10.1007/s00595-004-2985-0. Surg Today. 2005. PMID: 15976955
-
The protective effects of 17beta-estradiol on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat model, associated with regulation of heat-shock protein expression.J Surg Res. 2007 Jun 1;140(1):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.10.022. Epub 2007 Mar 2. J Surg Res. 2007. PMID: 17336333
-
Alpha-lipoic acid protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Pharmacology. 2007;79(3):163-70. doi: 10.1159/000098953. Epub 2007 Jan 24. Pharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17259747
Cited by
-
Exploring the drug repurposing potential of lisinopril against TNBS-induced colitis in Wistar rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04212-w. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40328912
-
Study of the protective effect of ischemic and pharmacological preconditioning on hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury induced in rats.JGH Open. 2017 Nov 14;1(3):105-111. doi: 10.1002/jgh3.12018. eCollection 2017 Nov. JGH Open. 2017. PMID: 30483545 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin ameliorates remote liver injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;17(2):169-73. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.2.169. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23626480 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of amlodipine, lisinopril and allopurinol on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats.Saudi Pharm J. 2016 Nov;24(6):635-644. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 May 19. Saudi Pharm J. 2016. PMID: 27829805 Free PMC article.
-
Paeonol Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 and TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 29;11(9):1687. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091687. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaeschke H. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G15–26. - PubMed
-
- Uhlmann D, Uhlmann S, Spiegel HU. Endothelin/nitric oxide balance influences hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2000;36(5 Suppl 1):S212–4. - PubMed
-
- Fiordaliso F, Cuccovillo I, Bianchi R, Bai A, Doni M, Salio M, et al. Cardiovascular oxidative stress is reduced by an ACE inhibitor in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Life Sci. 2006;79:121–9. - PubMed
-
- Desideri G, Grassi D, Croce G, Bocale R, Tiberti S, Evangelista S, et al. Different effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors on endothelin-1 and nitric oxide balance in human vascular endothelial cells: Evidence of an oxidant-sensitive pathway. Mediat Inflamm. 2008;2008:305087. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

