Sedative and antiepileptic effects of Anthocephalus cadamba Roxb. in mice and rats
- PMID: 22144777
- PMCID: PMC3229788
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.89829
Sedative and antiepileptic effects of Anthocephalus cadamba Roxb. in mice and rats
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the sedative and antiepileptic activities of ethanolic extract of Anthocephalus cadamba (ACE) bark in various experimental animal models.
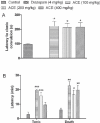
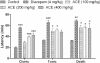
Materials and methods: ACE was tested at three doses viz. 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg p.o. We used ketamine-induced sleeping time model to test the sedative property of the extract where, onset and duration of sleep were observed. A paradigm of anticonvulsant models (pentylenetetrazole, isoniazid and maximal electroshock-induced seizures) were used to evaluate its protective effect against absence and generalized types of seizures. Onset of clonic convulsions, tonic extension and time of death were observed in PTZ and INH-induced seizure models. In MES model, duration of tonic hind leg extension and onset of stupor were observed.
Results: ACE showed significant increase in ketamine induced sleeping time. It also exhibited significant increase (P<0.05, 0.01 and 0.001) in latency to clonic convulsion, tonic extension and time of death in PTZ and INH models at all tested doses, whereas in the MES model, the lower dose was found to be effective when compared with the higher doses (200 and 400 mg/kg, p.o.).
Conclusion: The results of the present investigation demonstrated that ACE possesses sedative and antiepileptic activities.
Keywords: Anthocephalus cadamba; isoniazid; maximal electro shock; pentylenetetrazole; sedation; seizures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticonvulsant activity of alcoholic extract of bark of Pinus roxburghii Sarg.Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012 Sep;10(9):1056-60. doi: 10.3736/jcim20120915. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22979938
-
Anticonvulsant activities of Sambucus nigra.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jul;20(14):3123-6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27460744
-
Anticonvulsant potential of ethanol extracts and their solvent partitioned fractions from Flemingia strobilifera root.Pharmacognosy Res. 2013 Oct;5(4):265-70. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.118825. Pharmacognosy Res. 2013. PMID: 24174820 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous Extract of Wood Ear Mushroom, Auricularia polytricha (Agaricomycetes), Demonstrated Antiepileptic Activity against Seizure Induced by Maximal Electroshock and Isoniazid in Experimental Animals.Int J Med Mushrooms. 2019;21(1):29-35. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2018029113. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2019. PMID: 30806253
-
Effects of the non-NMDA antagonists NBQX and the 2,3-benzodiazepine GYKI 52466 on different seizure types in mice: comparison with diazepam and interactions with flumazenil.Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1349-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17146.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1994. PMID: 7889291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Insights about multi-targeting and synergistic neuromodulators in Ayurvedic herbs against epilepsy: integrated computational studies on drug-target and protein-protein interaction networks.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 22;9(1):10565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46715-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31332210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neurological disorders: Public health challenges. Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2006. Anonymous.
-
- Hegde K, Thakker SP, Joshi AB, Shastry CS, Chandrashekhar KS. Anticonvulsant activity of Carissa carandas Linn. root extract in experimental mice. Trop J Pharm Res. 2009;8:117–25.
-
- Mondal S, Dash GK, Acharyya A. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic studies of Neolamarckia cadamba barks. J Pharm Res. 2009;2:1133–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

