Polar flagellar biosynthesis and a regulator of flagellar number influence spatial parameters of cell division in Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 22144902
- PMCID: PMC3228812
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002420
Polar flagellar biosynthesis and a regulator of flagellar number influence spatial parameters of cell division in Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
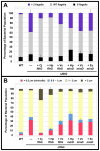
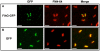
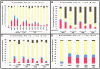
Spatial and numerical regulation of flagellar biosynthesis results in different flagellation patterns specific for each bacterial species. Campylobacter jejuni produces amphitrichous (bipolar) flagella to result in a single flagellum at both poles. These flagella confer swimming motility and a distinctive darting motility necessary for infection of humans to cause diarrheal disease and animals to promote commensalism. In addition to flagellation, symmetrical cell division is spatially regulated so that the divisome forms near the cellular midpoint. We have identified an unprecedented system for spatially regulating cell division in C. jejuni composed by FlhG, a regulator of flagellar number in polar flagellates, and components of amphitrichous flagella. Similar to its role in other polarly-flagellated bacteria, we found that FlhG regulates flagellar biosynthesis to limit poles of C. jejuni to one flagellum. Furthermore, we discovered that FlhG negatively influences the ability of FtsZ to initiate cell division. Through analysis of specific flagellar mutants, we discovered that components of the motor and switch complex of amphitrichous flagella are required with FlhG to specifically inhibit division at poles. Without FlhG or specific motor and switch complex proteins, cell division occurs more often at polar regions to form minicells. Our findings suggest a new understanding for the biological requirement of the amphitrichous flagellation pattern in bacteria that extend beyond motility, virulence, and colonization. We propose that amphitrichous bacteria such as Campylobacter species advantageously exploit placement of flagella at both poles to spatially regulate an FlhG-dependent mechanism to inhibit polar cell division, thereby encouraging symmetrical cell division to generate the greatest number of viable offspring. Furthermore, we found that other polarly-flagellated bacteria produce FlhG proteins that influence cell division, suggesting that FlhG and polar flagella may function together in a broad range of bacteria to spatially regulate division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Kusumoto A, Kamisaka K, Yakushi T, Terashima H, Shinohara A, et al. Regulation of polar flagellar number by the flhF and flhG genes in Vibrio alginolyticus. J Biochem. 2006;139:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Kusumoto A, Shinohara A, Terashima H, Kojima S, Yakushi T, et al. Collaboration of FlhF and FlhG to regulate polar-flagella number and localization in Vibrio alginolyticus. Microbiology. 2008;154:1390–1399. - PubMed
-
- Green JC, Kahramanoglou C, Rahman A, Pender AM, Charbonnel N, et al. Recruitment of the earliest component of the bacterial flagellum to the old cell division pole by a membrane-associated signal recognition particle family GTP-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 2009;391:679–690. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

