Drug discovery toward antagonists of methyl-lysine binding proteins
- PMID: 22145013
- PMCID: PMC3229088
- DOI: 10.2174/1875397301005010051
Drug discovery toward antagonists of methyl-lysine binding proteins
Abstract
The recognition of methyl-lysine and -arginine residues on both histone and other proteins by specific "reader" elements is important for chromatin regulation, gene expression, and control of cell-cycle progression. Recently the crucial role of these reader proteins in cancer development and dedifferentiation has emerged, owing to the increased interest among the scientific community. The methyl-lysine and -arginine readers are a large and very diverse set of effector proteins and targeting them with small molecule probes in drug discovery will inevitably require a detailed understanding of their structural biology and mechanism of binding. In the following review, the critical elements of methyl-lysine and -arginine recognition will be summarized with respect to each protein family and initial results in assay development, probe design, and drug discovery will be highlighted.
Keywords: Histones; chemical probes; chromatin; drug discovery.; methyl-arginine; methyl-lysine; pi-cation interactions; post-translational modifications; reader domains.
Figures


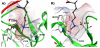
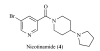
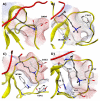


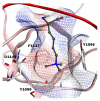
References
-
- Bhaumik SR, Smith E, Shilatifard A. Covalent modifications of histones during development and disease pathogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14:1008–16. - PubMed
-
- Wang GG, Allis CD, Chi P. Chromatin remodeling and cancer, Part I: Covalent histone modifications. Trends Mol Med. 2007;13:363–72. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–80. - PubMed
-
- Strahl BD, Allis CD. The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature. 2000;403:41–5. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Reinberg D. Transcription regulation by histone methylation: interplay between different covalent modifications of the core histone tails. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2343–60. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
