Runx1 loss minimally impacts long-term hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 22145044
- PMCID: PMC3228772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028430
Runx1 loss minimally impacts long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
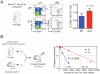
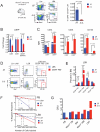
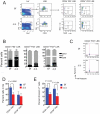
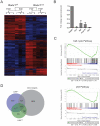
RUNX1 encodes a DNA binding subunit of the core-binding transcription factors and is frequently mutated in acute leukemia, therapy-related leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Mutations in RUNX1 are thought to confer upon hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) a pre-leukemic state, but the fundamental properties of Runx1 deficient pre-leukemic HSCs are not well defined. Here we show that Runx1 deficiency decreases both apoptosis and proliferation, but only minimally impacts the frequency of long term repopulating HSCs (LT-HSCs). It has been variously reported that Runx1 loss increases LT-HSC numbers, decreases LT-HSC numbers, or causes age-related HSC exhaustion. We attempt to resolve these discrepancies by showing that Runx1 deficiency alters the expression of several key HSC markers, and that the number of functional LT-HSCs varies depending on the criteria used to score them. Finally, we identify genes and pathways, including the cell cycle and p53 pathways that are dysregulated in Runx1 deficient HSCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Harada H, Harada Y, Tanaka H, Kimura A, Inaba T. Implications of somatic mutations in the AML1 gene in radiation-associated and therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome/acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:673–680. - PubMed
-
- Zharlyganova D, Harada H, Harada Y, Shinkarev S, Zhumadilov Z, et al. High frequency of AML1/RUNX1 point mutations in radiation-associated myelodysplastic syndrome around Semipalatinsk nuclear test site. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 2008;49:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Osato M, Asou N, Abdalla E, Hoshino K, Yamasaki H, et al. Biallelic and heterozygous point mutations in the Runt domain of the AML1/PEBP2αB gene associated with myeloblastic leukemias. Blood. 1999;93:1817–1824. - PubMed
-
- Kohlmann A, Grossmann V, Klein HU, Schindela S, Weiss T, et al. Next-generation sequencing technology reveals a characteristic pattern of molecular mutations in 72.8% of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia by detecting frequent alterations in TET2, CBL, RAS, and RUNX1. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3858–3865. - PubMed
-
- Kuo MC, Liang DC, Huang CF, Shih YS, Wu JH, et al. RUNX1 mutations are frequent in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and mutations at the C-terminal region might predict acute myeloid leukemia transformation. Leukemia. 2009;23:1426–1431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

