Attenuation of cytotoxic natural product DNA intercalating agents by caffeine
- PMID: 22145102
- PMCID: PMC3221498
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1107-19
Attenuation of cytotoxic natural product DNA intercalating agents by caffeine
Abstract
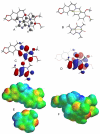
Many anti-tumor drugs function by intercalating into DNA. The xanthine alkaloid caffeine can also intercalate into DNA as well as form π-π molecular complexes with other planar alkaloids and anti-tumor drugs. The presence of caffeine could interfere with the intercalating anti-tumor drug by forming π-π molecular complexes with the drug, thereby blocking the planar aromatic drugs from intercalating into the DNA and ultimately lowering the toxicity of the drug to the cancer cells. The cytotoxic activities of several known DNA intercalators (berberine, camptothecin, chelerythrine, doxorubicin, ellipticine, and sanguinarine) on MCF-7 breast cancer cells, both with and without caffeine present (200 μg/mL) were determined. Significant attenuation of the cytotoxicities by caffeine was found. Computational molecular modeling studies involving the intercalating anti-tumor drugs with caffeine were also carried out using density functional theory (DFT) and the recently developed M06 functional. Relatively strong π-π interaction energies between caffeine and the intercalators were found, suggesting an "interceptor" role of caffeine protecting the DNA from intercalation.
Keywords: Caffeine; Cytotoxicity; DNA Intercalation; Density Functional Theory; π-π Complex.
Figures






References
-
- Sabisz M, Skladanowski A. Modulation of cellular response to anticancer treatment by caffeine: Inhbition of cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair and more. Curr Pharmaceut Biotechnol. 2008;9:325–336. http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/138920108785161497. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tragonos F, Kapuscinski J, Darzynkiewicz Z. Caffeine modulates the effects of DNA-intercalating drugs in vitro: A flow cytometric and spectrophotometric analysis of caffeine interaction with novantrone, doxorubicin, ellipticine, and the doxorubicin analogue AD198. Cancer Res. 1991;51:3682–3689. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2065324. - PubMed
-
- Davies DB, Veselkov DA, Djimant LN, Veselkov AN. Hetero-association of caffeine and aromatic drugs and their competitive binding with a DNA oligomer. Eur Biophys J. 2001;30:354–366. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s002490100150. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Larsen RW, Jasuja R, Hetzler RK, Muraoka PT, Andrada VG, Lameson DM. Spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies of caffeine complexes with DNA intercalators. Biophys J. 1996;70:443–452. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79587-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piosik J, Zdunek M, Kapuscinski J. The modulation by xanthines of the DNA-damaging effect of polycyclic aromatic agents. Part II. The stacking complexes of caffeine with doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;63:635–646. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-2952(01)00903-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
